Dec 18, 18 · Tyramine (TIEruhmeen) is an amino acid that helps regulate blood pressure It occurs naturally in the body, and it's found in certain foods Medications called monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) block monoamine oxidase, which is an enzyme that breaks down excess tyramine in the body Blocking this enzyme helps relieve depressionTyramine concen groups remained constant (Fig 2) trationi was measured in every specimen and the results are 3HTyramine metabolism In normal subjects, the showin in Fig 2 Halflife was determined by the least squares method from the loglinear terminal portion of the curveTyramine is a common component in many foods, and is normally rapidly metabolized by MAOAIndividuals not taking MAOIs may consume at least 2 grams of tyramine in a meal and not experience an increase in blood pressure, whereas those taking MAOIs such as tranylcypromine may experience a sharp increase in blood pressure following consumption of as little as 10 mg of tyramine
Neurotransmitters Table
Tyramine metabolism
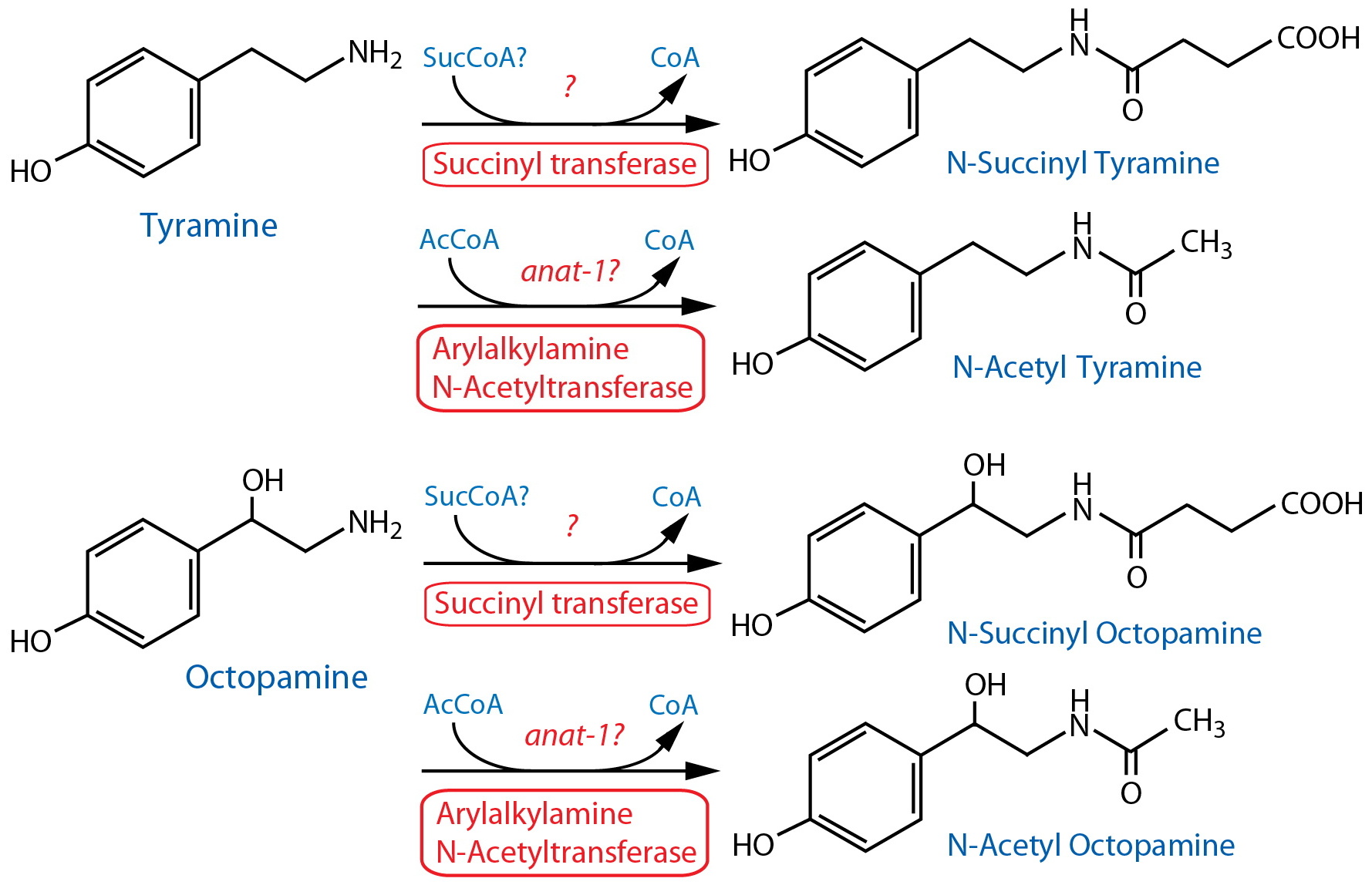
Tyramine metabolism-Tyramine and octopamine ruling behavior and metabolism Octopamine (OA) and tyramine (TA) are the invertebrate counterparts of the vertebrate adrenergic transmitters They are decarboxylation products of the amino acid tyrosine, with TA as the biological precursor of OA Nevertheless, both compounds are independent neurotransmitters that act through G prTyramine is a type of compound called a monoamine The body relies on an enzyme known as monoamine oxidase to break tyramine down Some people don't have enough monoamine oxidase to


Plos One A Multi Omic Systems Based Approach Reveals Metabolic Markers Of Bacterial Vaginosis And Insight Into The Disease
Three distinct metabolites of tyramine are produced by central nervous tissue of pharateadult Manduca sexta incubated in vitro with 3 HtyramineThe chemical identities of these metabolites have been sought by a combination of electrophoretic, chromatographic, hydrolyticThe induction of the phenylpropanoid pathway and of tyramine metabolism was monitored in cell suspension cultures of Nicotiana tabacum treated with cell wall‐degrading enzymes, in an attempt to correlate the synthesis of hydroxycinnamic acid amides of tyramine with the formation of wall‐bound phenolic polymers Treatment with commercial pectinase (from Penicilium occitanis )Jun 27, 19 · While levodopa metabolism likely limits drug availability and contributes to side effects, the potential ramifications of transforming dopamine into metatyramine are
The metabolism of tyramine by monoamine oxidase A/B causes oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA Monoamine oxidases A/B (EC 1434, MAO), flavoenzymes located on the outer mitochondrial membrane, catalyze the oxidative deamination of biogenic amines, such as dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrineMar 26, 1971 · Dietary Migraine and Tyramine Metabolism Abstract MIGRAINE afflicts some 10–15% of the population, which includes a subgroup of dietary migraine sufferers, all References Hanington, E, in Background to Migraine, Second Migraine Symp (edit by Smith, R) (Heinemann, London, AuthorJul 30, 16 · ADVERTISEMENTS The following points highlight the four main processes of Decarboxylation The processes are 1 Tyramine 2 Tryptamine 3 Histamine 4 GABA (γaminobutyric acid) Decarboxylation Process # 1 Tyramine i Tyramine is formed from tyrosine by tyrosine decarboxylation causing elevation of blood pressure ii This occurs in the gut by
Tyramine is a monoamine compound derived from the amino acid tyrosine Tyramine is metabolized by the enzyme monoamine oxidase In foods, it is often produced by the decarboxylation of tyrosine during fermentation or decay Foods containing considerable amounts of tyramine include fish, chocolate, alcoholic beverages, cheese, soy sauceDruginduced changes in the formation, storage and metabolism of tyramine in the mouse Juorio AV 1 The endogenous concentrations of p and mtyramine in the mouse striatum were determined by a mass spectrometric integrated ion current technique and concentrations were 213 and 61 ng/g, respectively2 The present results further confirm thatAbstract ▪ Abstract Octopamine (OA) and tyramine (TA) are the invertebrate counterparts of the vertebrate adrenergic transmitters They are decarboxylation products of the amino acid tyrosine, with TA as the biological precursor of OA Nevertheless, both compounds are independent neurotransmitters that act through G protein–coupled receptors


Systems Genomics Evaluation Of The Sh Sy5y Neuroblastoma Cell Line As A Model For Parkinson S Disease Bmc Genomics Full Text



Tyramine Tyramin Molecule It Is Monoamine Compound Derived Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image
Paratyramine, mydrial or uteramin) is a naturally occurring monoamine compound and trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine Tyramine acts by inducing the release of catecholamine An important characteristic of this product is its impediment to cross the bloodbrain barrier which restrains its side effects to only nonpsychoactiveJan 01, 1980 · Our experiments on the metabolism of tyramine in M sexta reinforce the idea that metabolic fates other than oxidative deamination predominate in conversions of monoamines in the insect CNS These studies have defined three distinct metabolites of tyramine produced by CNS tissue of the moth M sextaIt has indirect sympathomimetic action causing the release of stored catecholamines


Neurotransmitters Table


Tyrosine Metabolism Standard Metabolic Pathway
Oct 01, 1976 · By use of a sensitive and specific enzymatic isotopic method for the determination of tyramine, the small quantities of this amine which are present endogenously in rat tissues, including brain, heart, kidney and salivary gland, have been quantitated The levels of tyramine in brain were increased to a similar extent by injecting animals with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor, pargyline,Octopamine (OA) and tyramine (TA) are the invertebrate counterparts of the vertebrate adrenergic transmitters They are decarboxylation products of the amino acid tyrosine, with TA as the biological precursor of OA Nevertheless, both compounds are independent neurotransmitters that act through G protein–coupled receptors OA modulates a plethora of behaviors and peripheralMetabolism In humans, if monoamine metabolism is compromised by the use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and foods high in tyramine are ingested, a hypertensive crisis can result as tyramine can cause the release of stored monoamines, such as dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine The first signs of this were discovered by a neurologist


Neurotransmitters Table



Genetic Variation Within Adrenergic Pathways Determines In Vivo Effects Of Presynaptic Stimulation In Humans Circulation
Objective Episodic cluster headache is characterized by abnormalities in tyrosine metabolism (ie elevated levels of dopamine, tyramine, octopamine and synephrine and low levels of noradrenalin in plasma and platelets) It is unknown, however, if suchNov 13, · TYROSINE METABOLISM Tyrosine degradation is catalyzed by a series of five enzymatic reactions that yield acetoacetate, which is ketogenic, and the Krebs cycle intermediate fumarate, which is glucogenic The hepatocyte and renal proximal tubules are the only two cell types that express the complete pathway and contain sufficient quantities ofSep 24, 19 · The concentrations of ptyramine (pTA), mtyramine (mTA), dopamine (DA) and their principal metabolites, phydroxyphenylacetic acid (pHPAA), mhydroxyphenylacetic acid (mHPAA) and homovanillic acid (HVA) were determined in the corpus striatum of Swiss mice at various times after the subcutaneous administration of betaphenylethylamine (PE) (50 mg/kg)



Biochemical And Molecular Characterization Of Phenylacetate Coenzyme A Ligase An Enzyme Catalyzing The First Step In Aerobic Metabolism Of Phenylacetic Acid Inazoarcus Evansii Journal Of Bacteriology
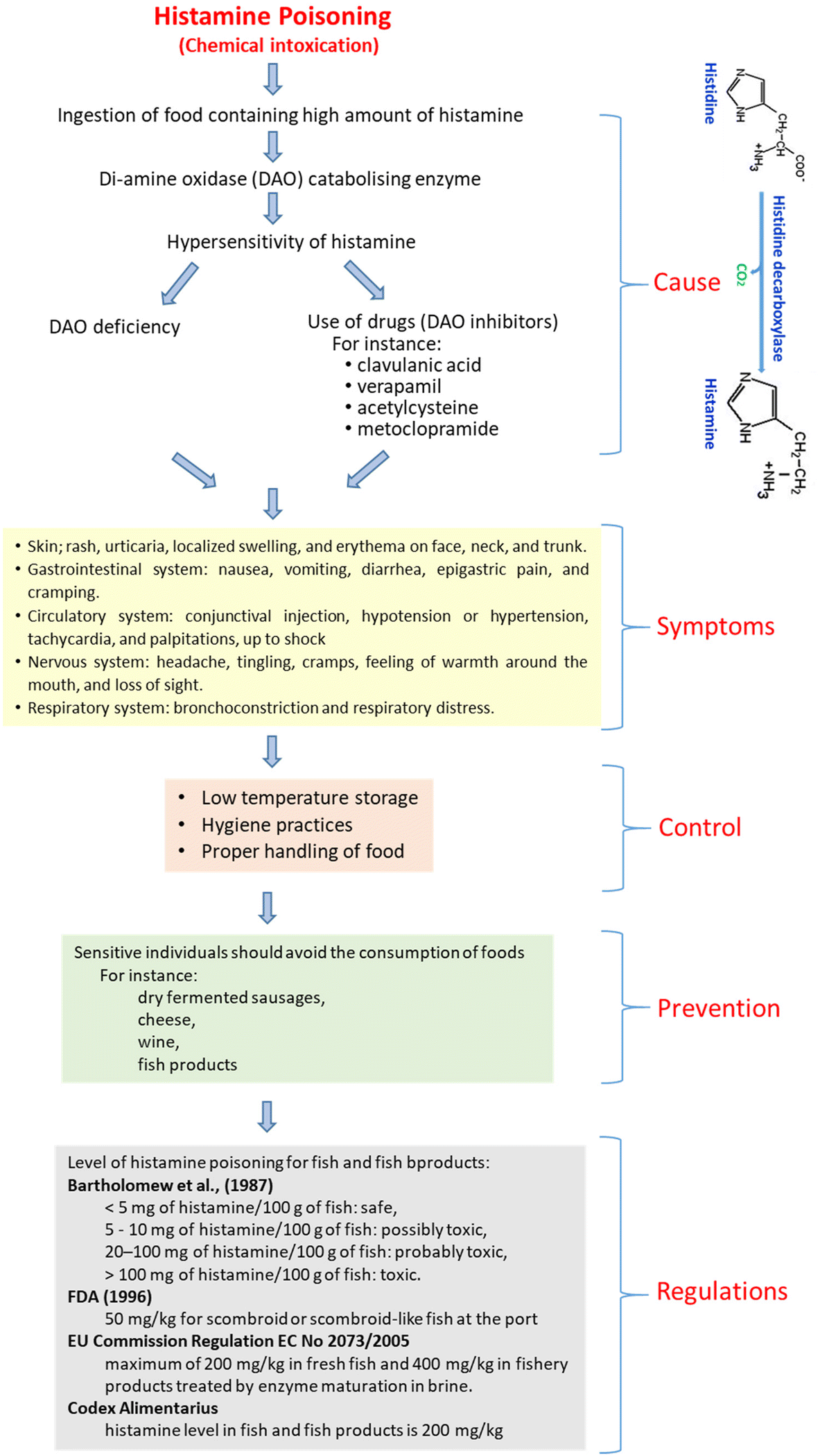


Chapter 1 Biogenic Amines Formation Toxicity Regulations In Food Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039
Your adrenal glands generallyThe ability of wine lactic acid bacteria to produce tyramine and phenylethylamine was investigated by biochemical and genetic methods An easy and accurate plate medium was developed to detect tyramineproducer strains, and a specific PCR assay thatOct 07, 14 · Identification and characterization of a tyramineglutamate ligase (MfnD) involved in methanofuran biosynthesis Wang Y(1), Xu H, Harich KC, White RH Author information (1)Department of Biochemistry, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University , Blacksburg, Virginia , United States



Biosynthetic And Metabolic Pathways Of Dopamine Dopamine Is Download Scientific Diagram
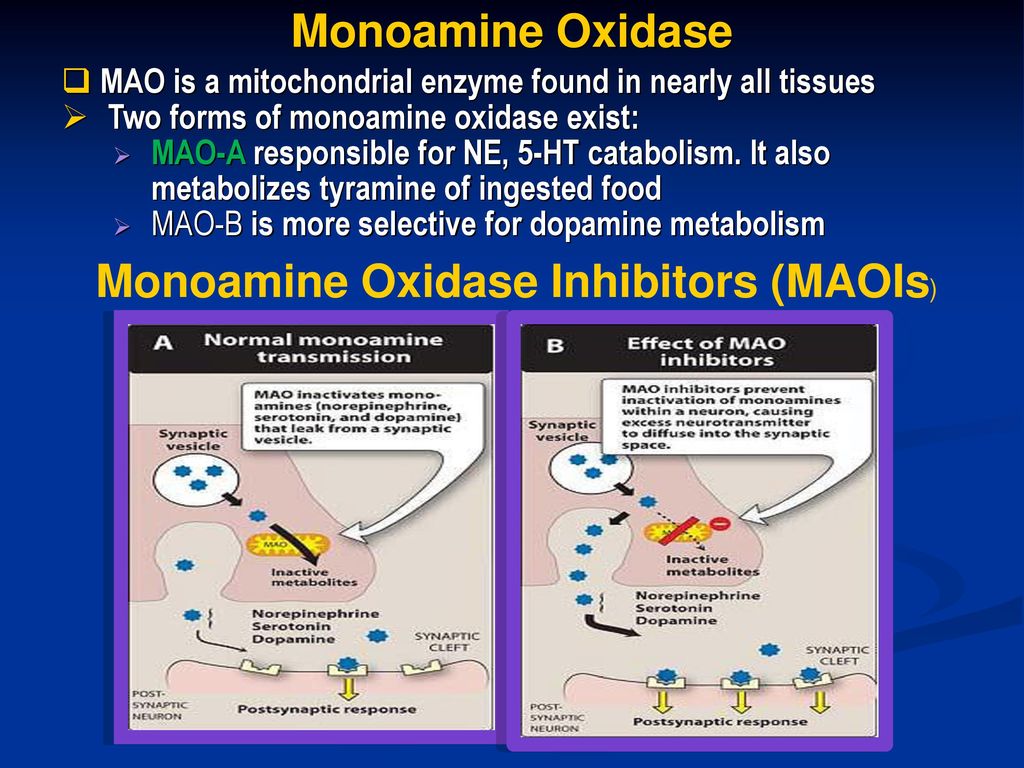


Drugs Used In Depression Prof Yieldez Bassiouni Ppt Download
The induction of the phenylpropanoid pathway and of tyramine metabolism was monitored in cell suspension cultures of Nicotiana tabacum treated with cell wall‐degrading enzymes, inSep 01, 1972 · Tyramine metabolism has been studied in the rat by Tacker et 2 using "C labelled material and by Lemberger3 in the rabbit A number of experiments were therefore carried out on both these species to test the general validity of the methodApr 01, · Octopamine (OA) and tyramine (TA) are closely related biogenic monoamines that act as signalling compounds in invertebrates, where they fulfil the roles played by adrenaline and noradrenaline in vertebrates Just like adrenaline and noradrenaline, OA and TA are extremely pleiotropic substances that regulate a wide variety of processes, including metabolic pathways



Neurotransmitters Table


Neurotransmitters Table
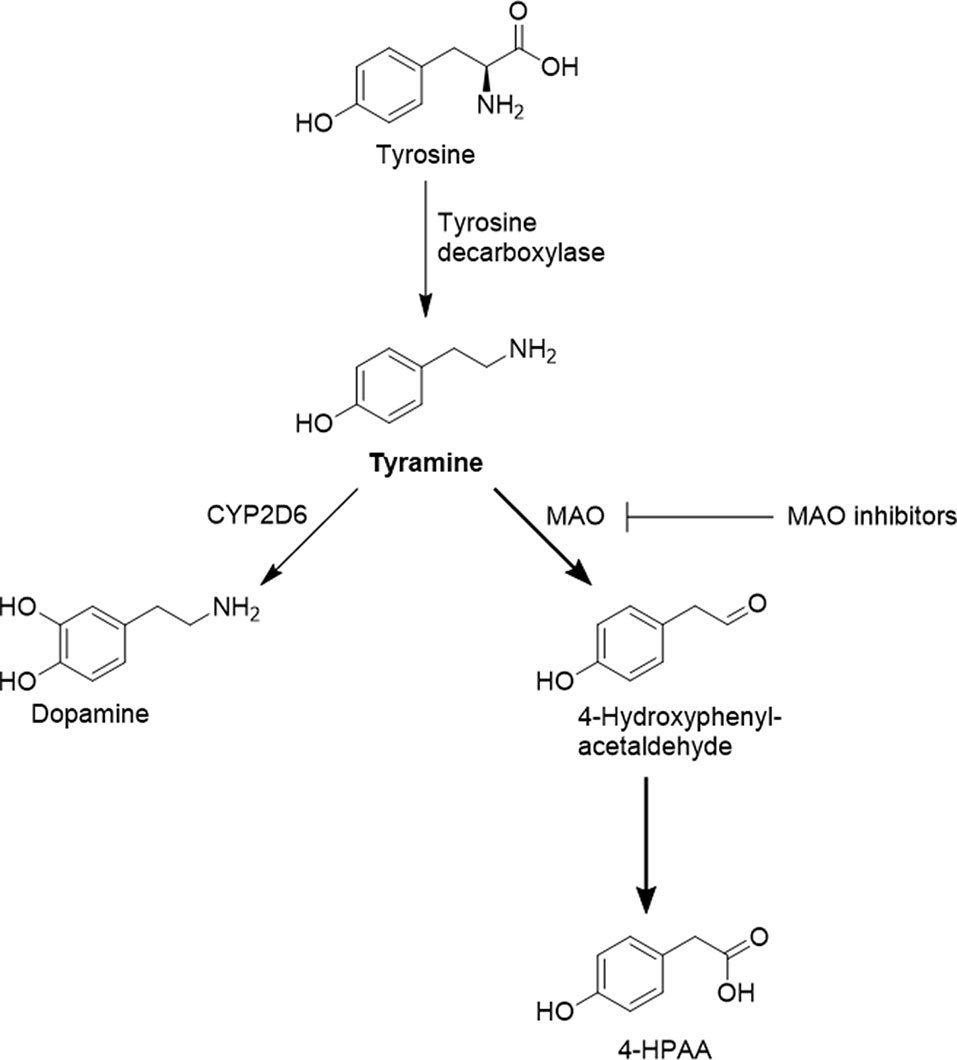
Oct 22, 04 · Effect of genetic polymorphism on the metabolism of endogenous neuroactive substances, progesterone and ptyramine, catalyzed by CYP2D6 Niwa T(1), Hiroi T, Tsuzuki D, Yamamoto S, Narimatsu S, Fukuda T, Azuma J, Funae YNotes MAOItype antidepressants will prevent the metabolism of tyramine, which is present in blue cheese & beer Tyramine in such foods is normally metabolized by MAO in the gut before it can be absorbed MAO inhibitors prevent this breakdown, resulting in elevated tyramine levels after ingestion of such foodsJun 25, 04 · The contribution of the MAO metabolism of tyramine to induce hydroxyl radical formation in vivo seems to be of particular importance because recently it has been demonstrated in vitro that mitochondrial lesions were caused by MAOinduced monoamine metabolism and that the metabolism of tyramine by MAOA/B led to oxidative damage of the


Plos One A Multi Omic Systems Based Approach Reveals Metabolic Markers Of Bacterial Vaginosis And Insight Into The Disease



Figure 1 From Analysis Of Neuroactive Amines In Fermented Beverages Using A Portable Microchip Capillary Electrophoresis System Semantic Scholar
LTyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteinsIt is a nonessential amino acid with a polar side groupThe word "tyrosine" is from the Greek tyrós, meaning cheese, as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheeseOct 01, 07 · However, other studies, using similar doses of tyramine in humans, have demonstrated that tyramine's action requires NE release For example, the acute pressor effect of tyramine is inhibited by duloxetine, a compound that inhibits tyramine uptake into, and therefore subsequent NE release from, nerve terminals Thus, in humans, tyramine'sFeb 01, 1970 · These results indicate that tyramine metabolism is altered by ethanol in the same way as the metabolism of sero tonin and norepinephrine1'3 An increase in the NADH/NAD ratio caused by ethanol which in creases the reduction of the intermediate aldehyde and decreases its oxidation, and a competitive inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase by



Octopamine Regulates Sleep In Drosophila Through Protein Kinase A Dependent Mechanisms Journal Of Neuroscience



Adrenergic Drugs Prezentaciya Onlajn
Feb 01, 1980 · Dog saphenous vein strips were perifused and exposed to seven concentrations of tyramine, ranging from 15 μM to 108 mM during 25 min Fractional release of tritium (determined during and after the exposure to tyramine) was directly proportional to the concentration of tyramine However, the percentage contribution by noradrenaline, normetanephrine andNov 15, 1996 · The intramitochondrial H 2 O 2 ss calculated in terms of glutathione peroxidase activity during the metabolism of tyramine was 48fold higher (771 ± 025 × 10 −7 M) than that obtained during the oxidation of succinate via complex II in the presence of antimycin A (164 ± 02 × 10 −8 M) Oxidative damage to the brain mtDNA wasMECHANISM Tyramine is a byproduct of Tyrosine metabolism by MAO in the liver Typically it will have low bioavailability due to extensive firstpass effect in the liver If the patient is taking a MOA inhibitor, Tyramine accumulates in the bloodstream;



Extensive Reprogramming Of Primary And Secondary Metabolism By Fungal Elicitor Or Infection In Parsley Cells Semantic Scholar


Decarboxylation To Tyramine A Major Route Of Tyrosine Metabolism In Mammals Abstract Europe Pmc
Monoamine oxidases (MAO) (EC 1434) are a family of enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of monoamines, employing oxygen to clip off their amine group They are found bound to the outer membrane of mitochondria in most cell types of the body The first such enzyme was discovered in 1928 by Mary Bernheim in the liver and was named tyramine oxidase The MAOs belong to theTyramine Drug Class Indirectly Acting Sympathomimetic (a byproduct of tyrosine metabolism) Mechanism of Action Tyramine is taken up into nerve terminals by NET (the norepinephrine reuptake transporter) and causes the release of catecholamines It has been proposed that this results from reverse transport of NET (Broadley, 10)Mar 01, 1971 · Because of this significant correlation, we decided to investigate the metabolism of tyramine in normal and dietary migraine subjects using large doses of tyramine and, separately, tracer doses of 14 Ctyramine MIGRAINE afflicts some 1015% of the population, which includes a subgroup of dietary migraine sufferers, all of whom specifically
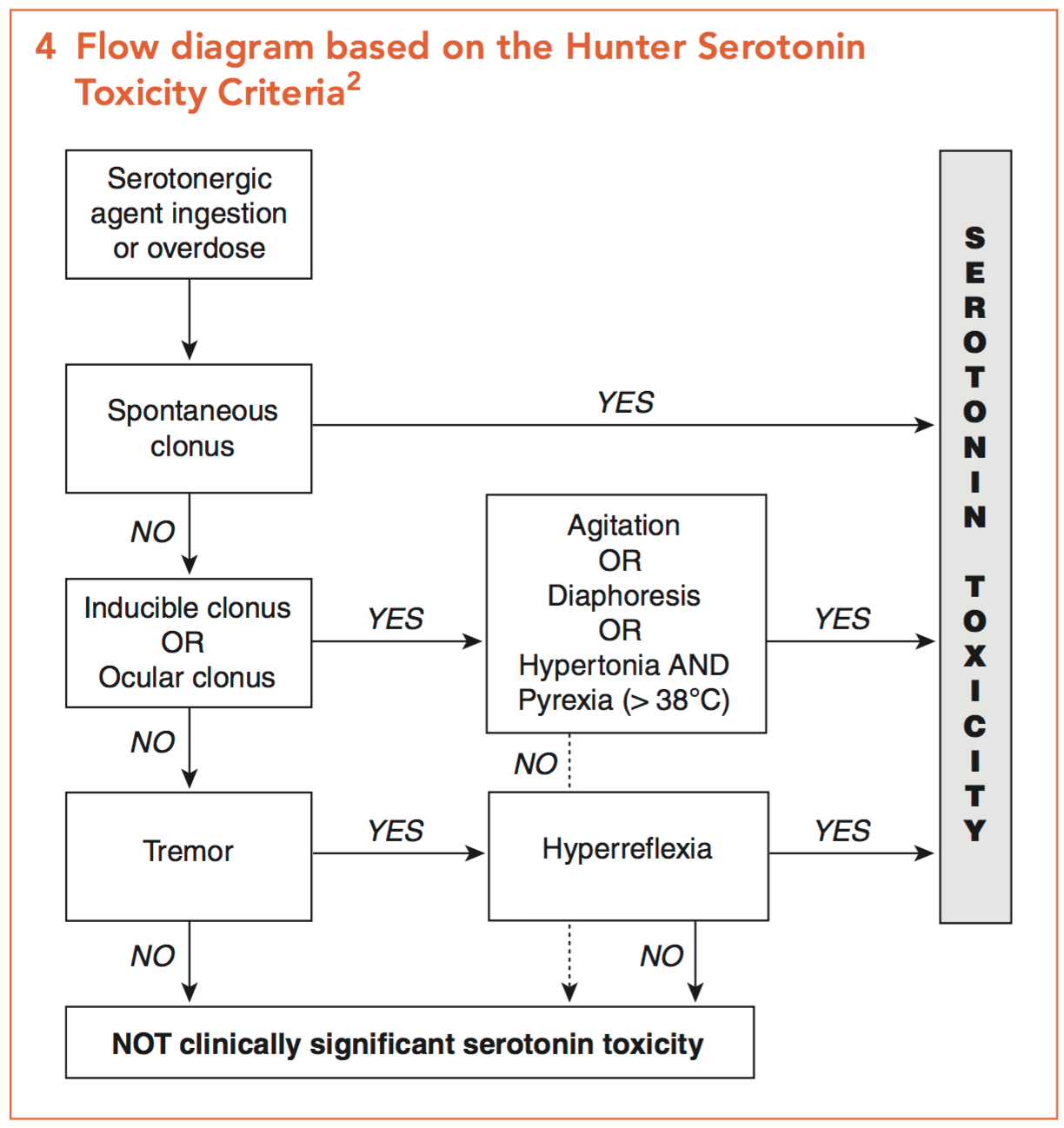


Maoi Toxicity Litfl Toxicology Library Toxicants
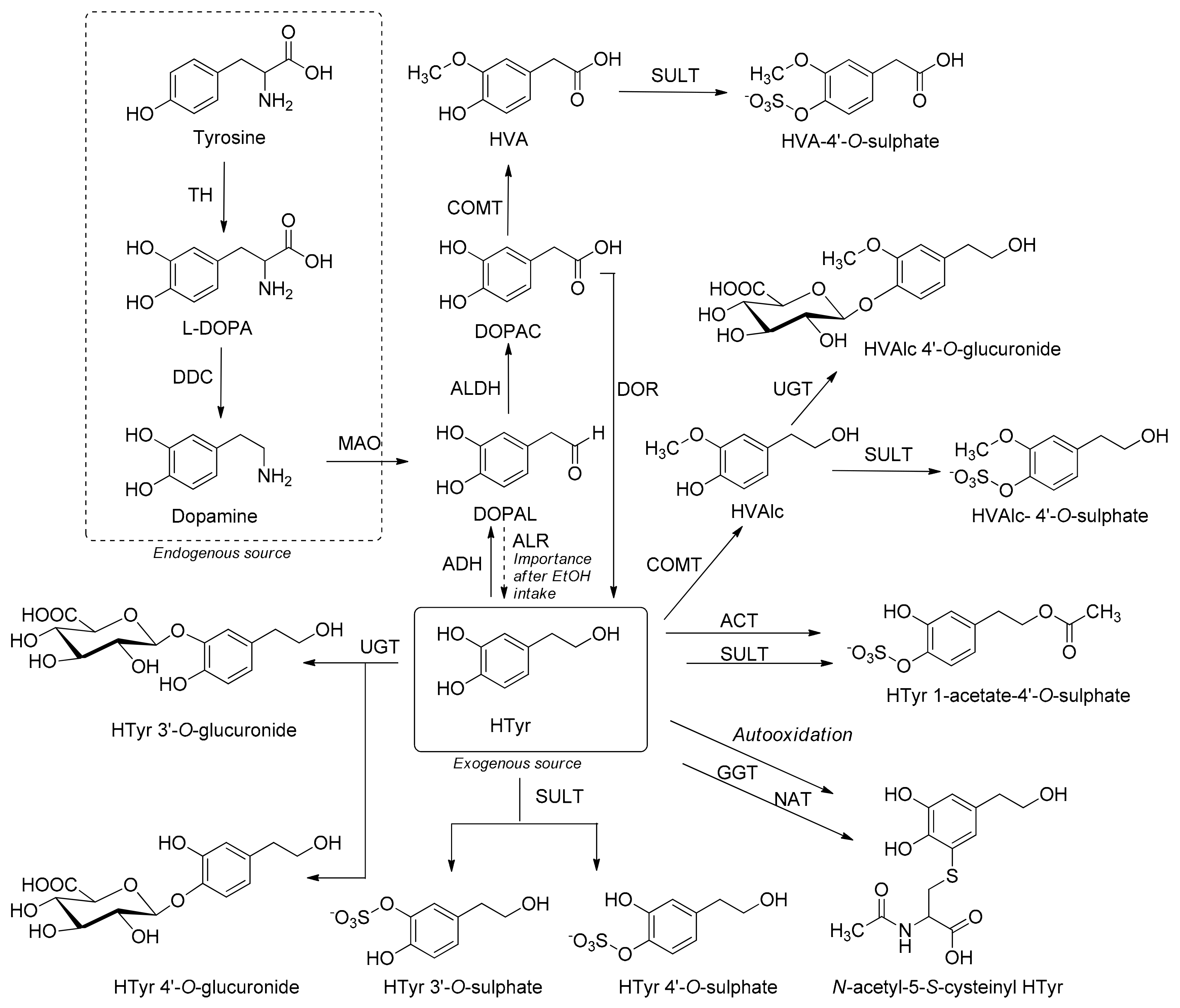


Molecules Free Full Text Hydroxytyrosol Tyrosol And Derivatives And Their Potential Effects On Human Health Html
The thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) help regulate growth and metabolism in the body It's important that T3 and T4 levels are neither too high nor too low SupplementingFeb 01, 19 · Tyramine is a compound produced by the breakdown of an amino acid called tyrosine It's naturally present in some foods, plants, and animals What does tyramine do?Abstract By use of a sensitive and specific enzymatic isotopic method for the determination of tyramine, the small quantities of this amine which are present endogenously in rat tissues, including brain, heart, kidney and salivary gland, have been quantitated The levels of tyramine in brain were increased to a similar extent by injecting animals with a monoamine oxidase



Taar1 Dependent And Independent Actions Of Tyramine In Interaction With Glutamate Underlie Central Effects Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Biological Psychiatry



Bioavailability Ppt Download
The phenolamines tyramine and octopamine are decarboxylation products of the amino acid tyrosine Although tyramine is the biological precursor of octopamine, both compounds are independent neurotransmitters, acting through various Gprotein coupled receptors Especially, octopamine modulates a plethora of behaviors, peripheral and sense organsJun 04, · But when the enzyme is inhibited by MAOIs, tyramine metabolism is inhibited, and the amino acid may build up to excessive levels As levels of tyramine rise, a person can experience high blood pressure, headaches, heart problems, nausea, vomiting, visual problems, and confusion 3Tyramine slows the metabolism of these drugs and can result in a dangerous rise in blood pressure The most wellpublicized fooddrug interaction of late has certainly been that of grapefruit juice and a virtual pharmacopeia of drugs But some experts say its effects are still occasionally underestimated According to Hollenberg, drinking just



Biochemistry Of Plant Phenolics Metabolism Of The Aromatic Amino Acids By Fungi Pdf Document



Tyramine Tyrosine Metabolism Page 1 Line 17qq Com
Tyrosine metabolism In preshunted dogs, the plasma tyramine levels determined over a period of 36 hr after the oral dose of ttyrosine did not change appreciably from the endogenous levels (fig 2, right panel) Postop eratively, there was a progressive increase in the sys temic bioavailability of tyramine &r oral administra



Shikimate Pathway Wikipedia



Tyramine Tyrosine Metabolism Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Evolution Of Dispersal Syndrome And Its Corresponding Metabolomic Changes Biorxiv



Tyramine Tyrosine Metabolism Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Metabolic Recruitment Of Spinal Locomotion Intracellular Neuromodulation By Trace Amines And Their Receptors Hochman S Neural Regen Res



Beyond Brown Polyphenol Oxidases As Enzymes Of Plant Specialized Metabolism Topic Of Research Paper In Biological Sciences Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub



Tranylcypromine Wikipedia



Tyramine Metabolism Page 1 Line 17qq Com



The Main Steps Of Levodopa Metabolism And Important Therapeutic Targets Download Scientific Diagram
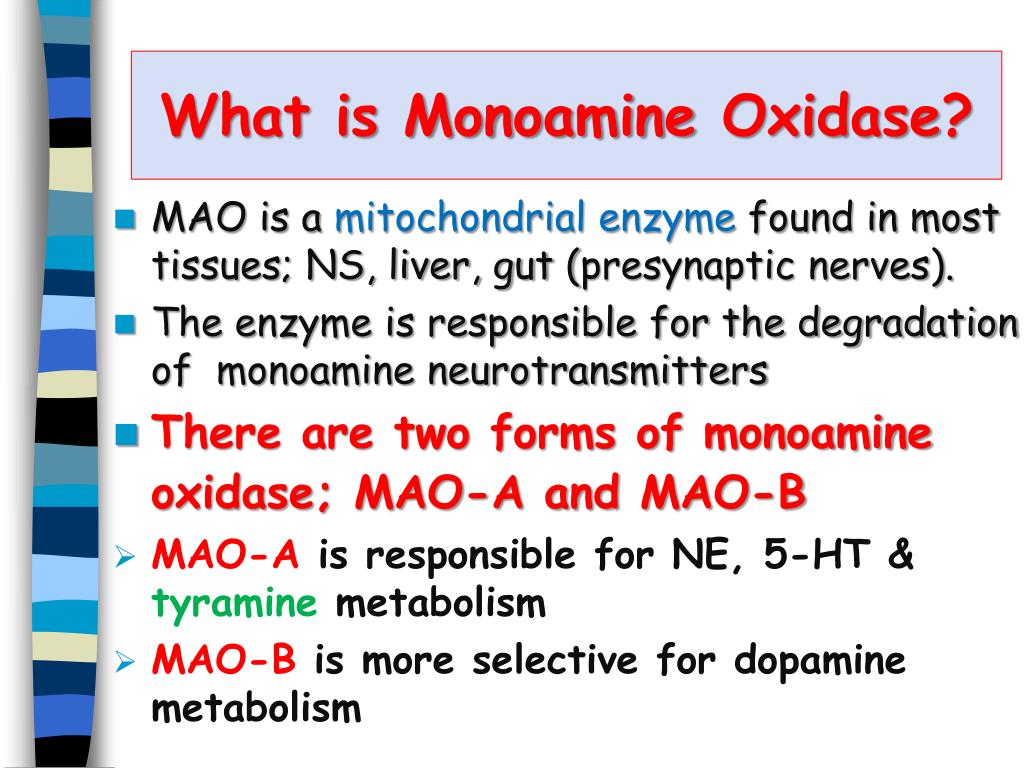


Ppt Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Welcome Cns Stimulants 2 Dr Dana Ameen Ppt Download



Ppt Drug Metabolism Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Tyramine Metabolism Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Catabolism Of Biogenic Amines In Pseudomonas Species Luengo Environmental Microbiology Wiley Online Library
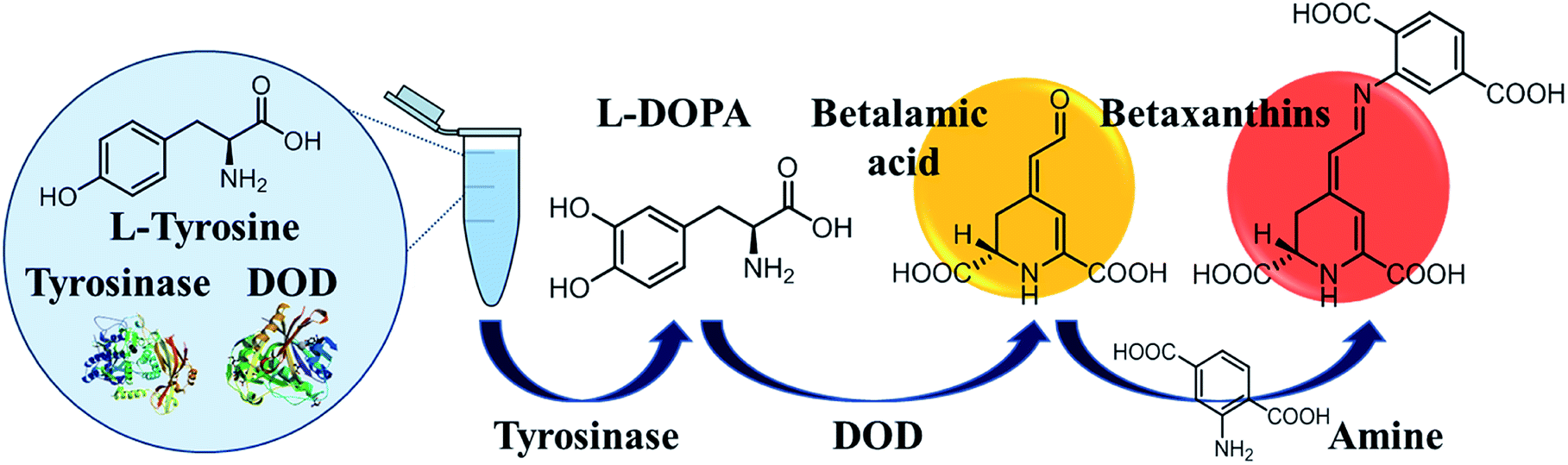


Detection Of Tyrosine And Monitoring Tyrosinase Activity Using An Enzyme Cascade Triggered Colorimetric Reaction Rsc Advances Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D0raf



Meta Tyramine Wikipedia



Enhanced Formation Of Aromatic Amino Acids Increases Fragrance Without Affecting Flower Longevity Or Pigmentation In Petunia Hybrida Oliva 15 Plant Biotechnology Journal Wiley Online Library



Electrochemical Methods For The In Vitro Assessment Of Drug Metabolism Intechopen



Discovery And Inhibition Of An Interspecies Gut Bacterial Pathway For Levodopa Metabolism Science



A Review Of The Mechanisms And Role Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors In Parkinson S Disease Neurology



Tyramine Metabolism Page 1 Line 17qq Com
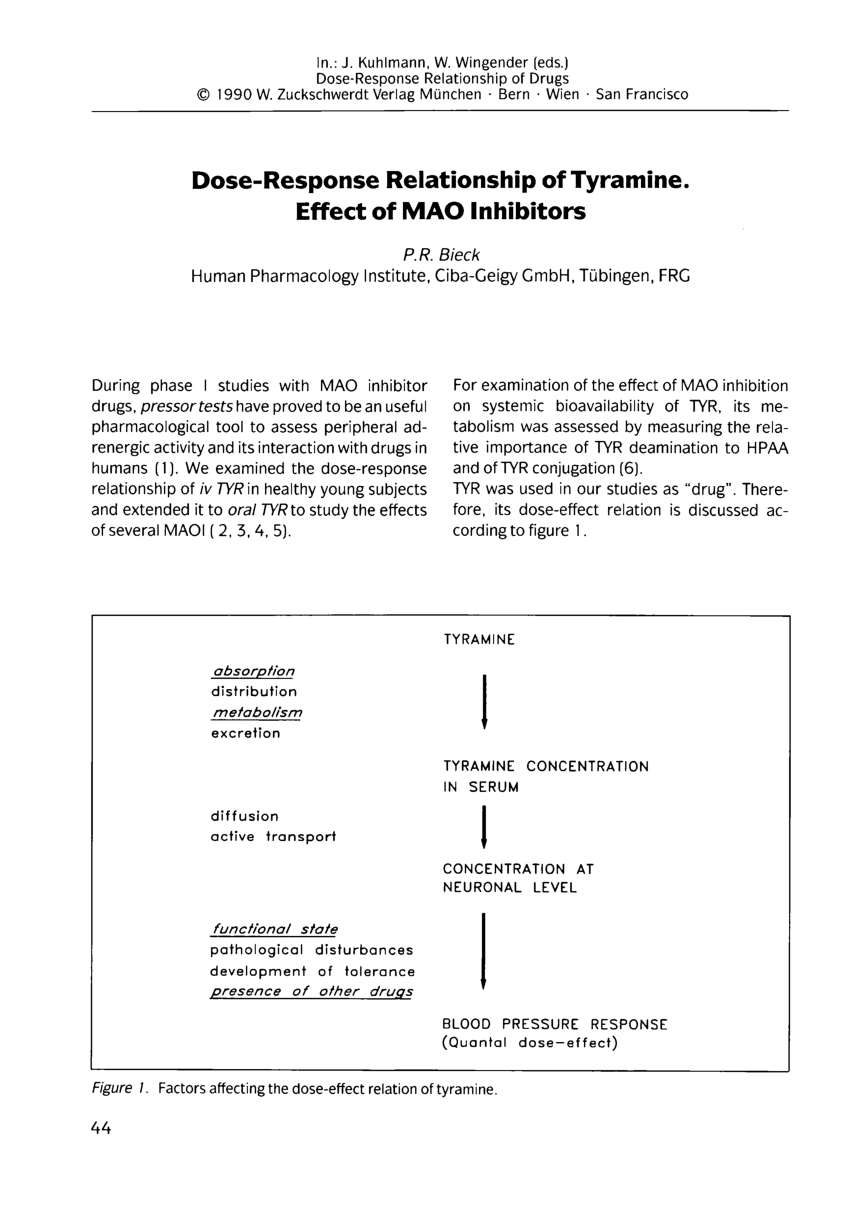


Pdf Dose Response Relationship Of Tyramine Effect Of Mao Inhibitors
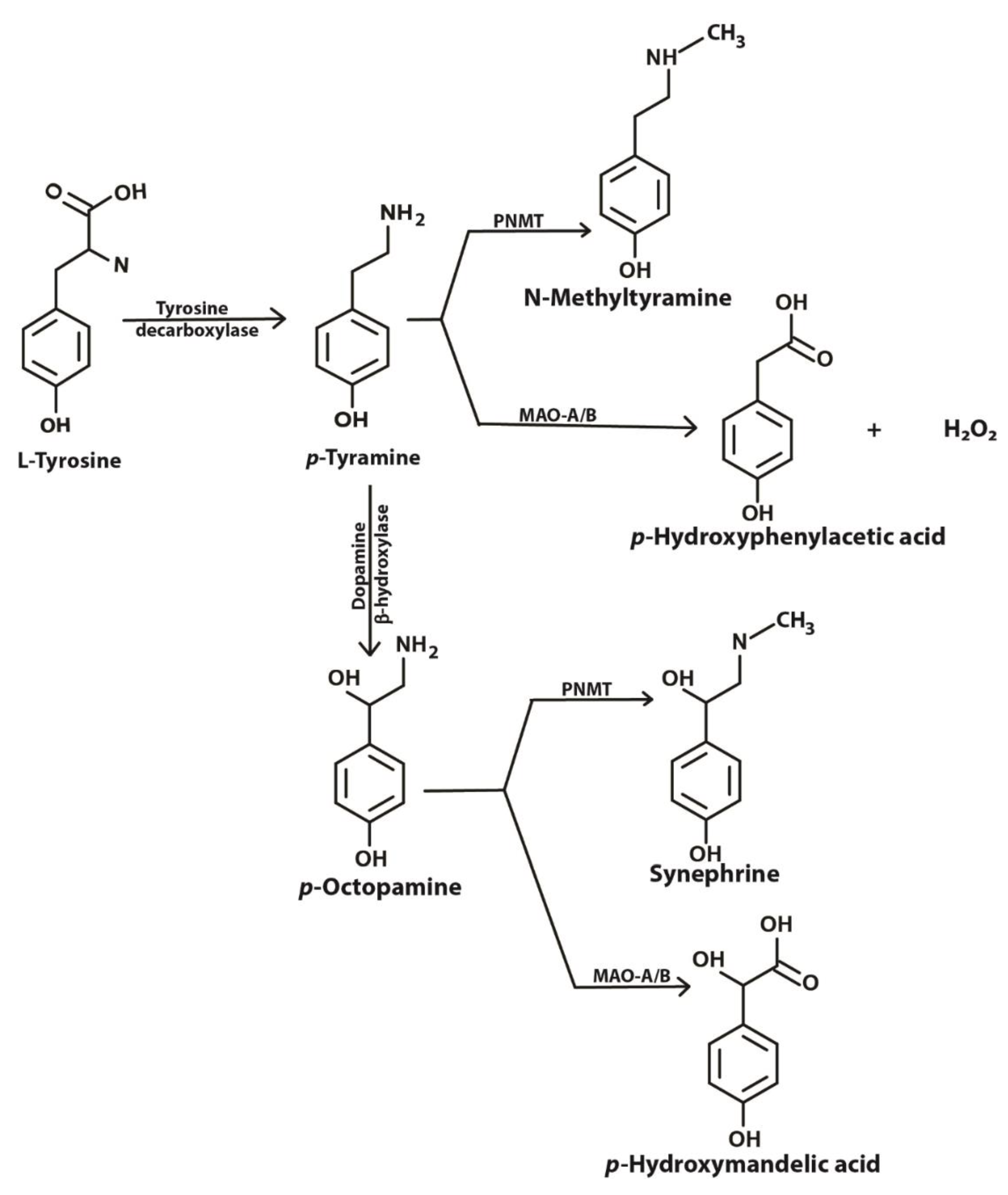


Biomedicines Free Full Text Tyramine And Amyloid Beta 42 A Toxic Synergy Html



Tyramine Wikipedia
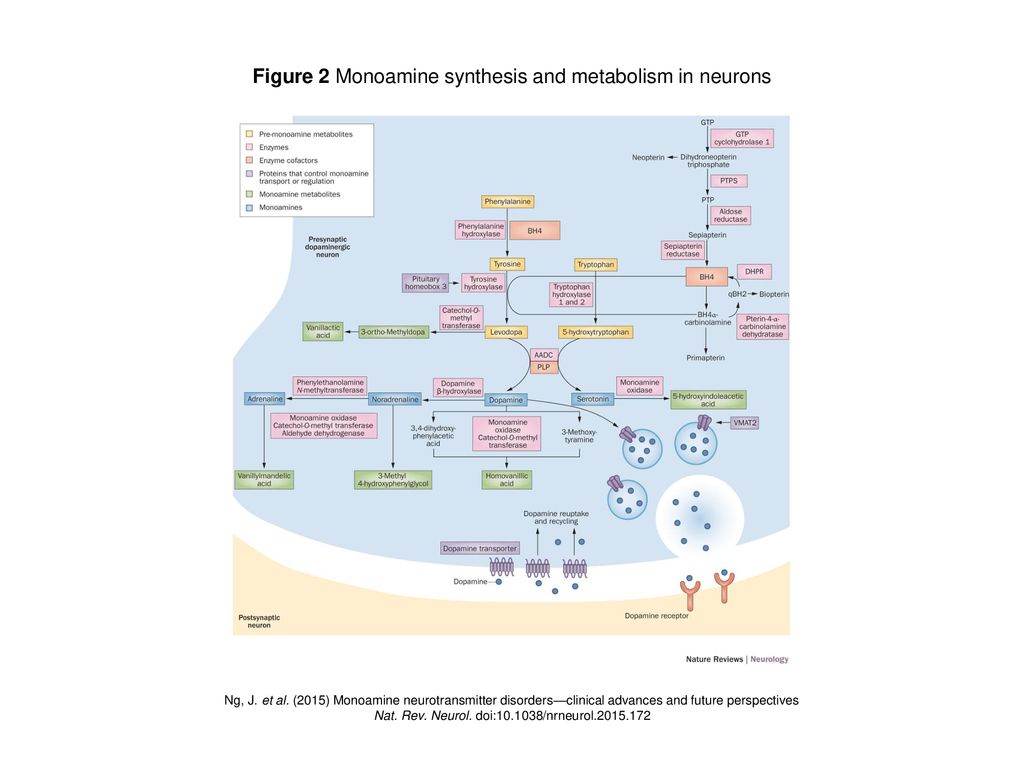


Figure 2 Monoamine Synthesis And Metabolism In Neurons Ppt Download



Tyramine And Octopamine Independently Inhibit Serotonin Stimulated Aversive Behaviors In Caenorhabditis Elegans Through Two Novel Amine Receptors Journal Of Neuroscience



Tyramine Action On Motoneuron Excitability And Adaptable Tyramine Octopamine Ratios Adjust Drosophila Locomotion To Nutritional State Pnas



Find Out Why There Are Dietary Restrictions For People Taking Maoi Antidepressants And Which Tyramine Rich Foods You Will Ne Healthy Cheese Metabolic Diet Food



Review Mechanisms Of How The Intestinal Microbiota Alters The Effects Of Drugs And Bile Acids Drug Metabolism Disposition



Pdf Metabolic Profiling Reveals The Protective Effect Of Diammonium Glycyrrhizinate On Acute Hepatic Injury Induced By Carbon Tetrachloride Semantic Scholar
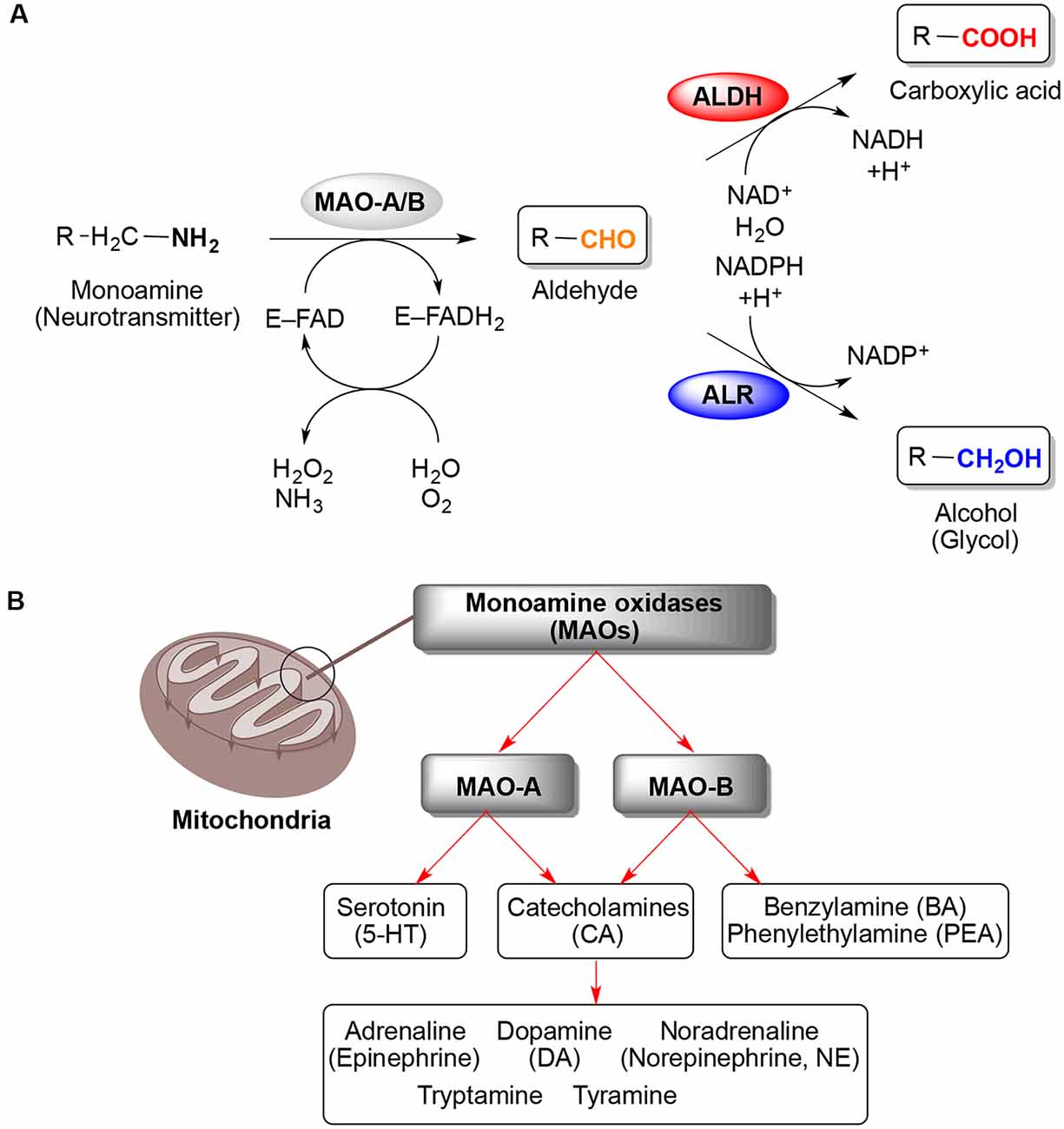


Frontiers Monoamine Oxidases Maos As Privileged Molecular Targets In Neuroscience Research Literature Analysis Molecular Neuroscience



Tyramine Metabolism Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Taar1 Dependent And Independent Actions Of Tyramine In Interaction With Glutamate Underlie Central Effects Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Biological Psychiatry
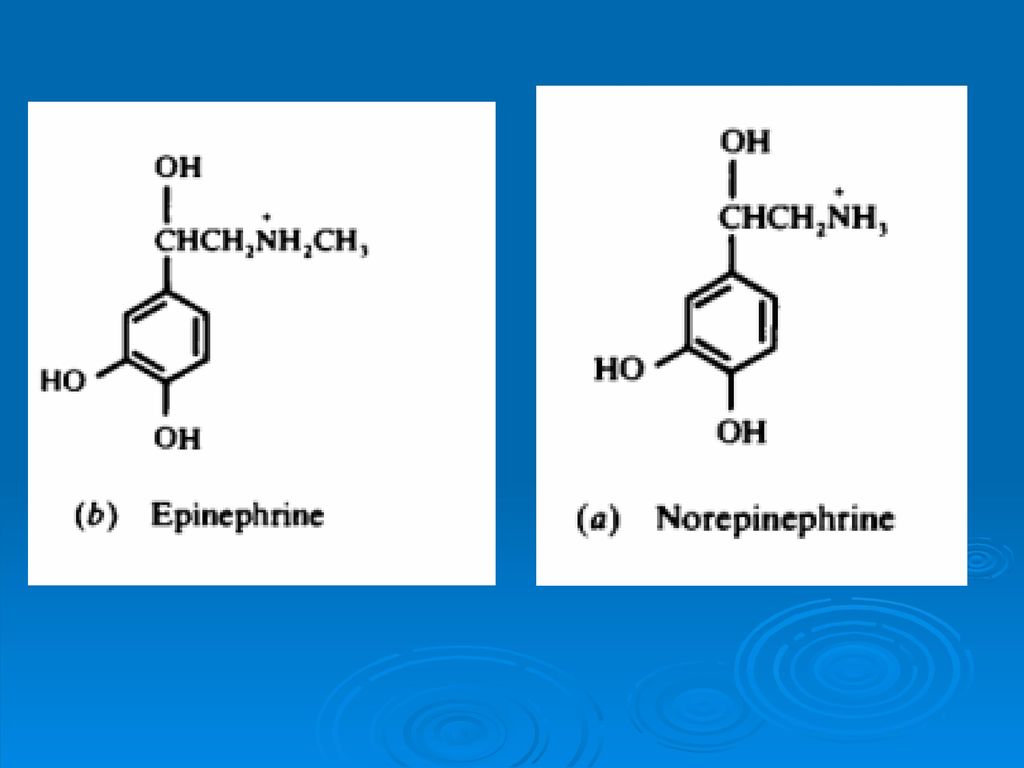


Amino Acids Metabolism Ppt Download
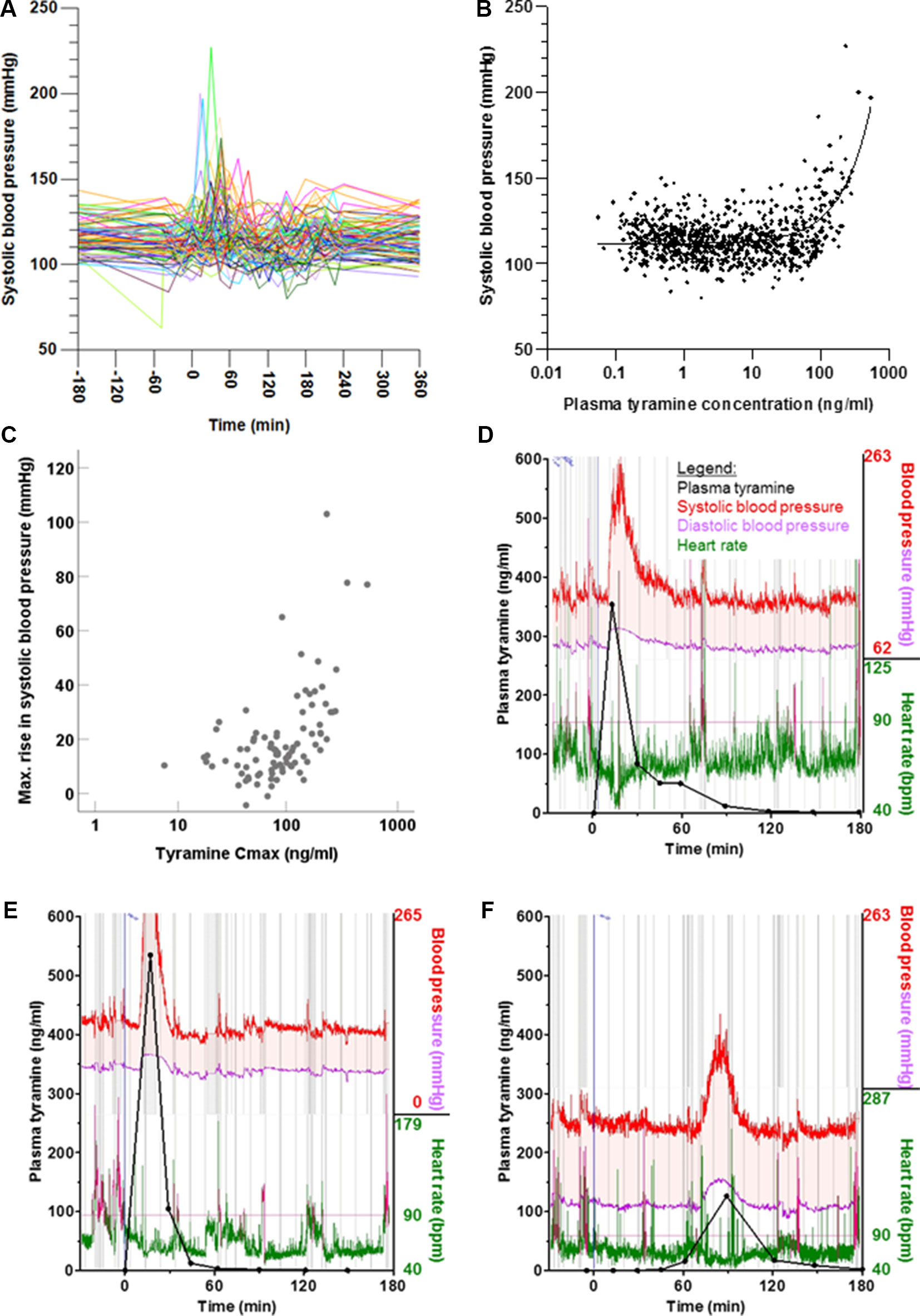


Frontiers Highly Variable Pharmacokinetics Of Tyramine In Humans And Polymorphisms In Oct1 Cyp2d6 And Mao A Pharmacology



Harvard Researchers Find Gut Microbes Can Lessen Effectiveness Of Medicines Worddisk


Novel Roles For The Polyphenol Oxidase Enzyme In Secondary Metabolism And The Regulation Of Cell Death In Walnut Plant Physiology



Pdf Metabolism Of Tyramine On Subjects Treated With Different Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors



Evolution Of Dispersal Syndrome And Its Corresponding Metabolomic Changes Biorxiv



Tyramine Functions Independently Of Octopamine In The Caenorhabditis Elegans Nervous System Neuron



Tyrosine Metabolism Enzymes Coenzymes 1 Aromatic L Amino Acid Download Scientific Diagram



Taar1 Dependent And Independent Actions Of Tyramine In Interaction With Glutamate Underlie Central Effects Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Biological Psychiatry


Pharmacological Treatment Of Parkinson S Disease Exon Publications
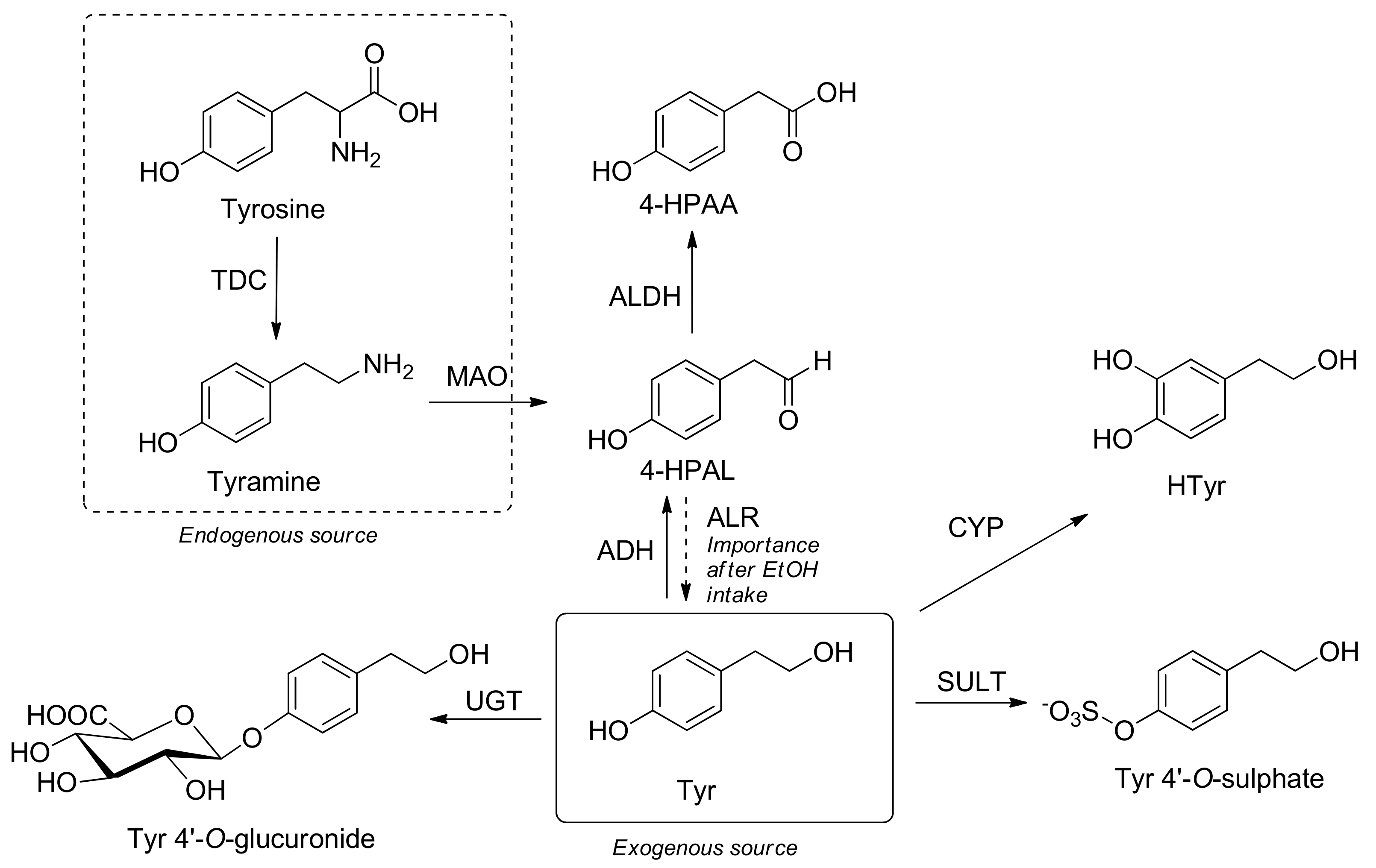


7i9auenu Eotum


Ans 16 Amphetamine Tyramine Cocaine Ephedrine And Pseudoephedrine Youtube


Frontiers Highly Variable Pharmacokinetics Of Tyramine In Humans And Polymorphisms In Oct1 Cyp2d6 And Mao A Pharmacology



Tyramine Tyrosine Metabolism Page 1 Line 17qq Com
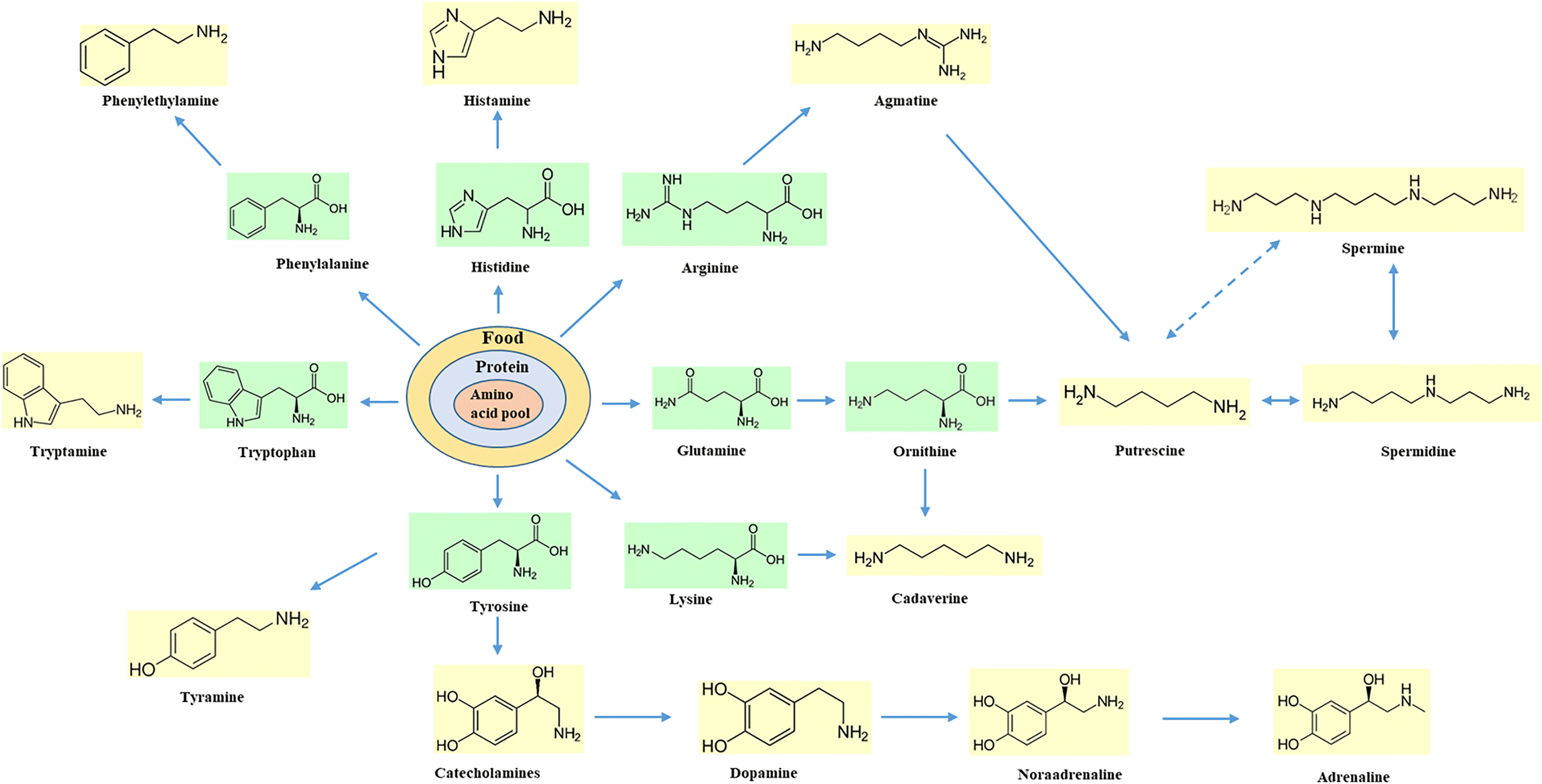


Chapter 1 Biogenic Amines Formation Toxicity Regulations In Food Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039



Histamine In Food Dr Healthcare Innovating In Dao Deficiency Through Medical Nutrition



Serotonin Syndrome A Brief Review Cmaj


Decarboxylation To Tyramine A Major Route Of Tyrosine Metabolism In Mammals Abstract Europe Pmc



Parkinson Disease Levodopa And The Gut Microbiota When Microbiology Meets Pharmacology Brussow Environmental Microbiology Wiley Online Library
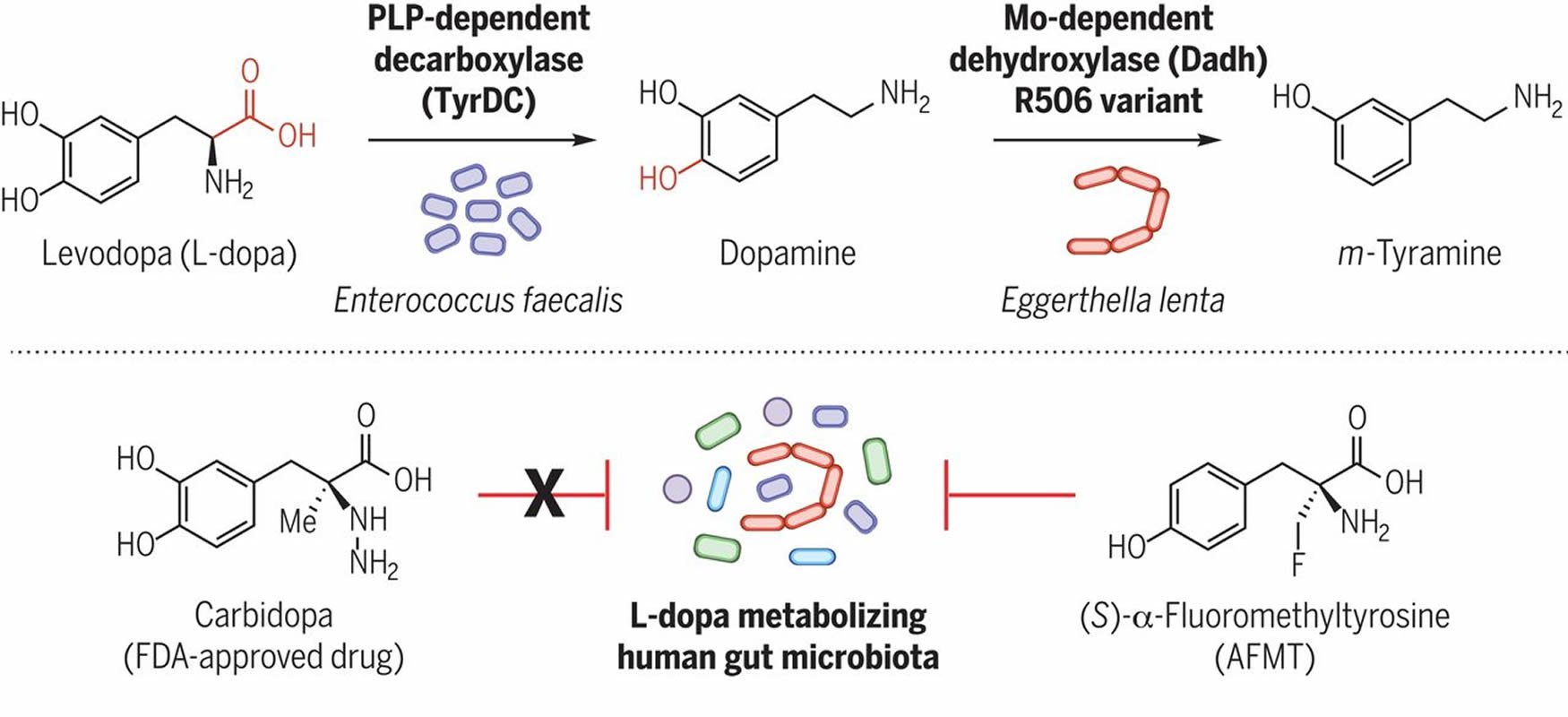


Gut Bacteria Interferes With Metabolism Of Parkinson S Drug Neuroscience News



Pdf Genetic Phytochemical And Bioactivity Studies Of Clinacanthus Nutans Burm F Lindau Acanthaceae Semantic Scholar



High Throughput Metabolomics Reveals The Perturbed Metabolic Pathways And Biomarkers Of Yang Huang Syndrome As Potential Targets For Evaluating The Therapeutic Effects And Mechanism Of Geniposide
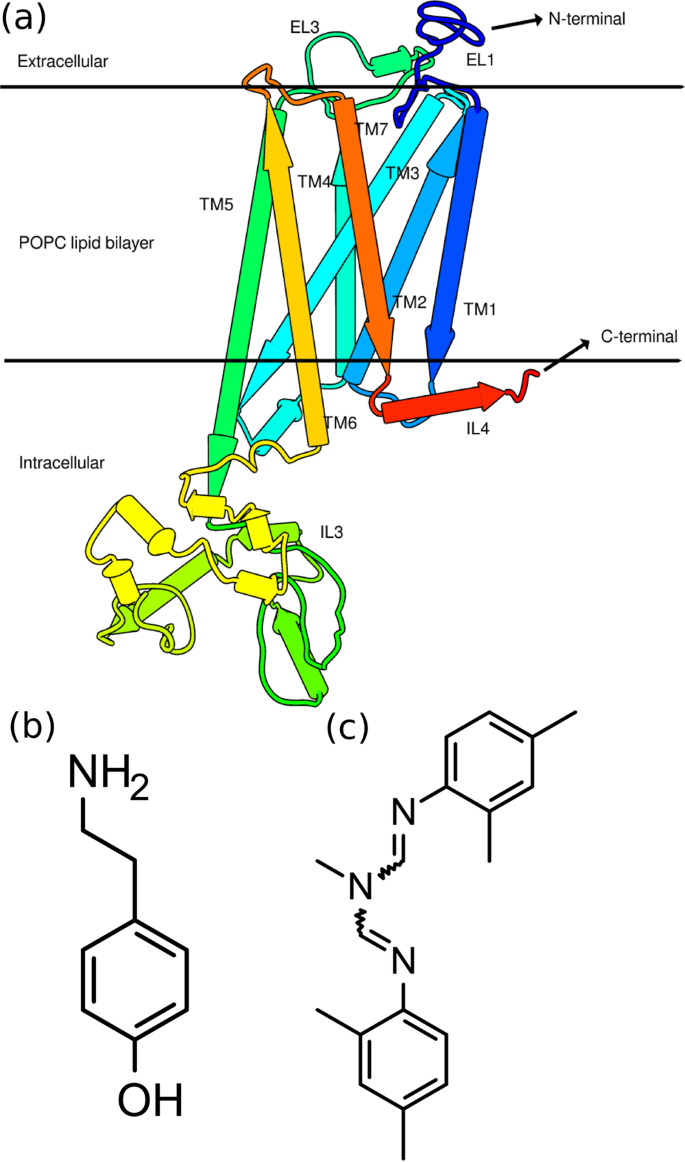


Ligand Induced Conformational Dynamics Of A Tyramine Receptor From Sitophilus Oryzae Scientific Reports



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿