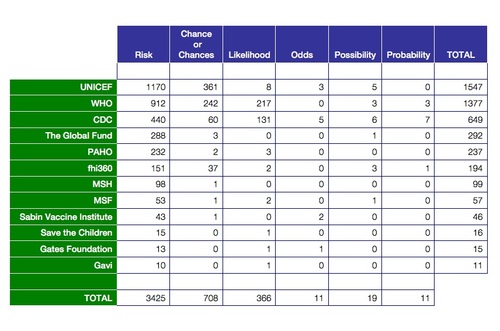
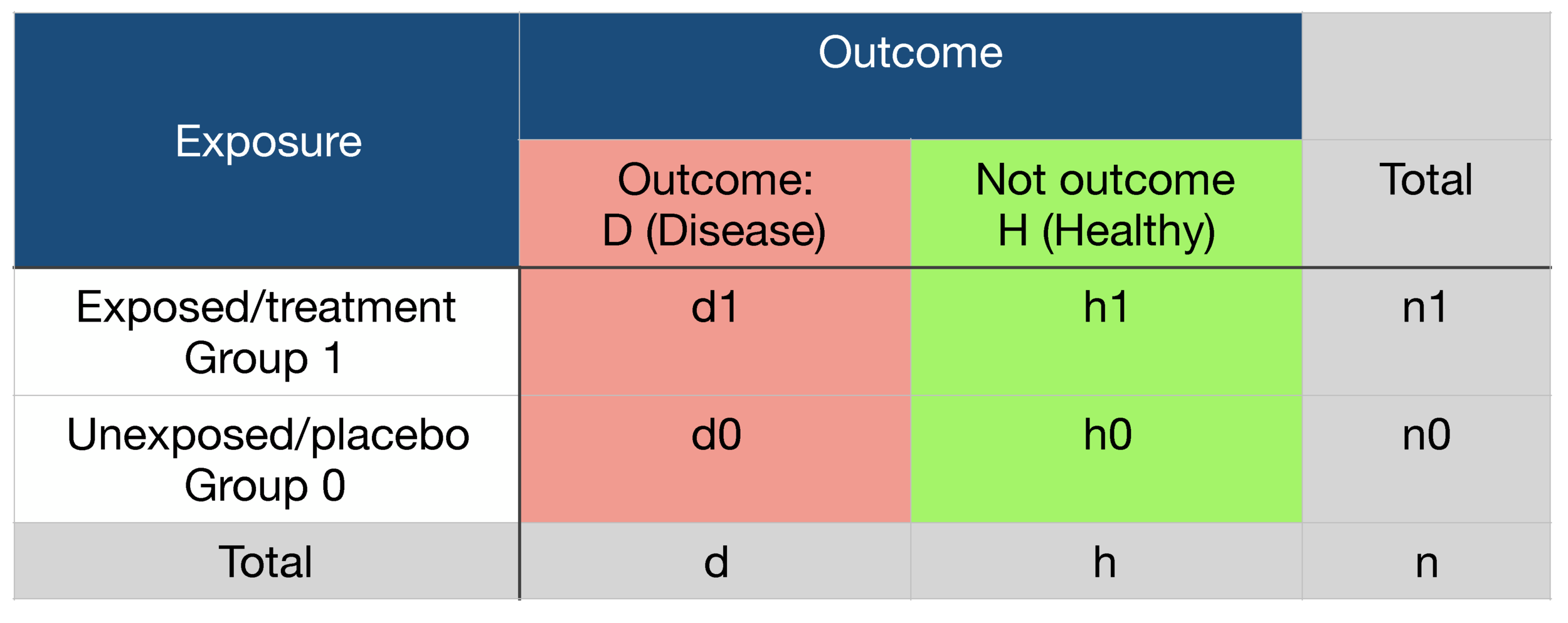
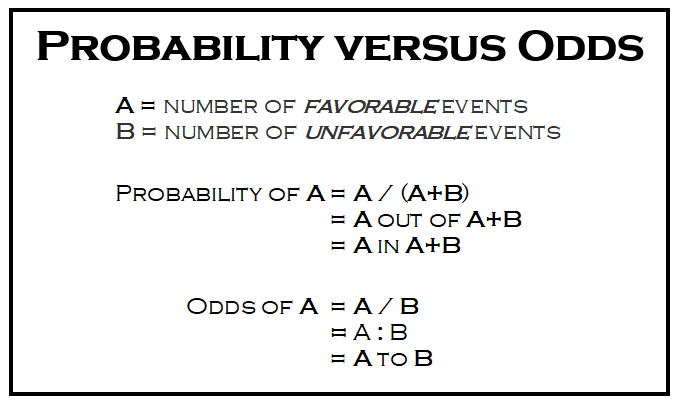
Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed to the treatment Odds is the number having the outcome divided by the number not having the outcome Risk and risk ratios are more commonly used than odds and odds ratios in medicine as these are much more intuitive Risk describes the probability of an event occurring In medicine this is often an undesirable health outcome or adverse event Odds ratio = (A*D) / (B*C) The relative risk tells us the ratio of the probability of an event occurring in a treatment group to the probability of an event occurring in a control group It is calculated as Relative risk = A/ (AB) / C/ (CD) In short, here's the difference An odds ratio is a ratio of two odds
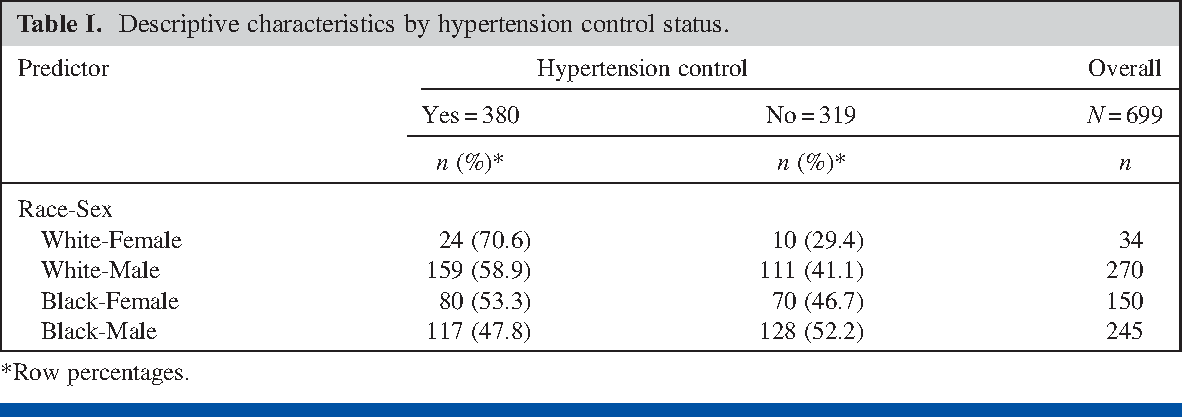
Table I From Prevalence Odds Ratio Versus Prevalence Ratio Choice Comes With Consequences Semantic Scholar
Odds versus risk
Odds versus risk-Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) If we go a step further, we can calculate the ratio between the two risks, called relative risk or risk ratio (RR), which indicates how much more likely is the occurrence of the event in one group compared with the other group Meanwhile, the odds represents a quite different concept The odds indicates how much more likely is an event to occur than not to occur (p/ (1p))




Relative Risk Wikipedia
An odds ratio greater than 1 indicates that the disease more likely to occur in the group than the group Similarly, an odds ratio less than 1 indicates that the disease is less likely to occur in the group For example an odds ratio of 2 indicates that people from the group had twice the risk of having the disease as people from the groupRISK AND ODDS DEFINITIONS "Risk" refers to the probability of occurrence of an event or outcome Statistically, risk = chance of the outcome of interest/all possible outcomes The term "odds" is often used instead of risk "Odds" refers to the probability of occurrence of an event/probability of the event not occurring then the odds ratio is computed by taking the ratio of odds, where the odds in each group is computed as follows OR = (a/b) / (c/d) As with a risk ratio, the convention is to place the odds in the unexposed group in the denominator
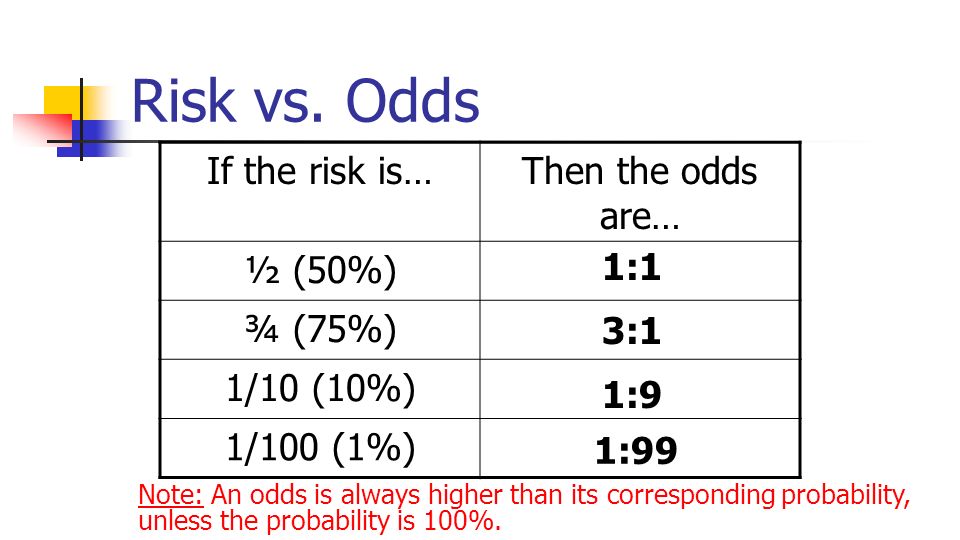
That is one of the attractive features of the odds ratio — when the health outcome is uncommon, the odds ratio provides a reasonable approximation of the risk ratio Another attractive feature is that the odds ratio can be calculated with data from a casecontrol study, whereas neither a risk ratio nor a rate ratio can be calculated The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programAnd a risk of 095 is equivalent to odds of 19
For instance, odds are a symmetric measure, meaning that while risk only examines outcomes given interventions, odds can also examine interventions given outcomes Thus, a study can be constructed where, rather than choosing trial groups and measuring outcomes, outcomes can be chosen, and other factors can be analyzedRather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not The odds ratio is a common measure of risk but its interpretation may be hazardous The risk ratio is a ratio of probabilities, which are themselves ratios The numerator of a probability is the number of cases with the outcome, and the denominator is the total number of cases




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube
In biomedical research, we are often interested in quantifying the relationship between an exposure and an outcome "Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables In this article, which is the fourth in the series of common pitfalls in statistical analysis, we explain the meaning of risk and odds and the difference between the twoBMJ 14;348g1407 doi /bmjg1407 (Published 7 February 14) Page 1 of 2 Endgames ENDGAMES STATISTICAL QUESTION Relative risks versus odds ratios Philip Sedgwick reader in medical statistics and medical education Centre for Medical and Healthcare Education, St George's, University of London, London, UK Researchers investigated the effectiveness of a probiotic drink Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;




Relative Risk Wikipedia



Risk Of Death By Age And Sex
It turns out that odds ratio can be an approximation of the relative risk when the latter cannot be calculated For example In casecontrol studies when the risk of a disease cannot be knownWhen events are common, as is often the case in clinical trials, the differences between odds and risks are large For example, a risk of 05 is equivalent to an odds of 1; For instance, odds are a symmetric measure, meaning that while risk only examines outcomes given interventions, odds can also examine interventions given outcomes Thus, a study can be constructed where, rather than choosing trial groups and measuring outcomes, outcomes can be chosen, and other factors can be analyzed




Solved Question 8 8 33 Out Of 8 33 Points The Odds Ratio Chegg Com




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




Pdf Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk




Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To
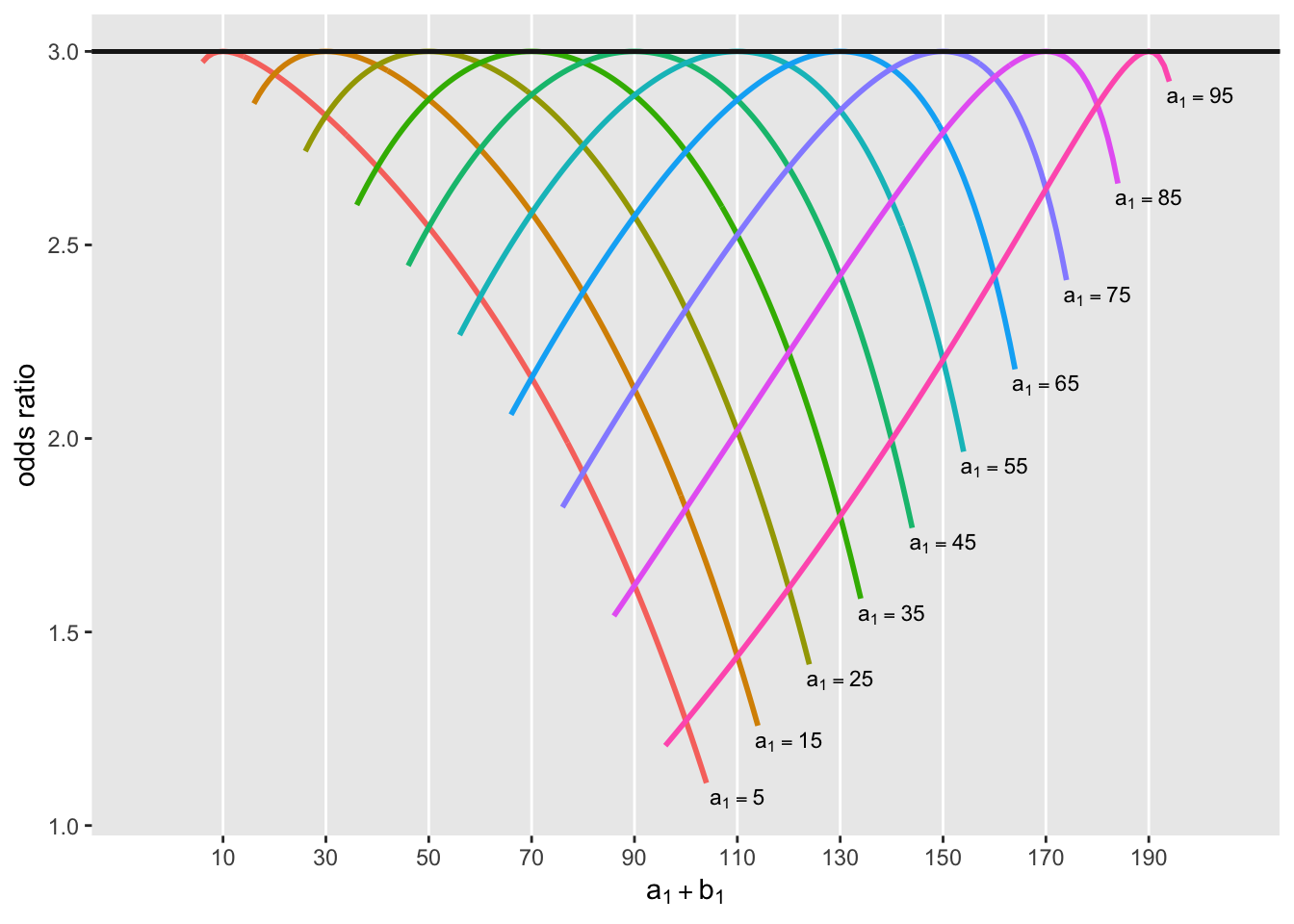



How The Odds Ratio Confounds A Brief Study In A Few Colorful Figures Our Data Generation




Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk Ranganathan P Aggarwal R Pramesh C S Perspect Clin Res




How To Read American Odds In Sports Betting The Action Network




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Measures Of Disease Association Measuring Occurrence Of New Outcome Events Can Be An Aim By Itself But Usually We Want To Look At The Relationship Between Ppt Download



Link Springer Com
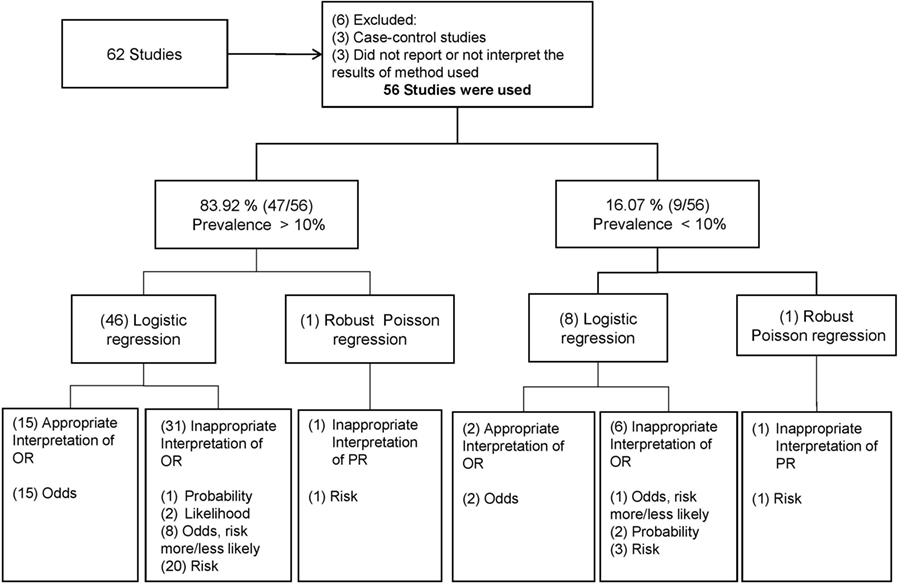



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science



印刷可能 Odds Vs Risk ただの悪魔の画像




Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February




Pooled Odds Ratio Or Of Risk Of Mortality In Vitamin D Deficient Download Scientific Diagram



2



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
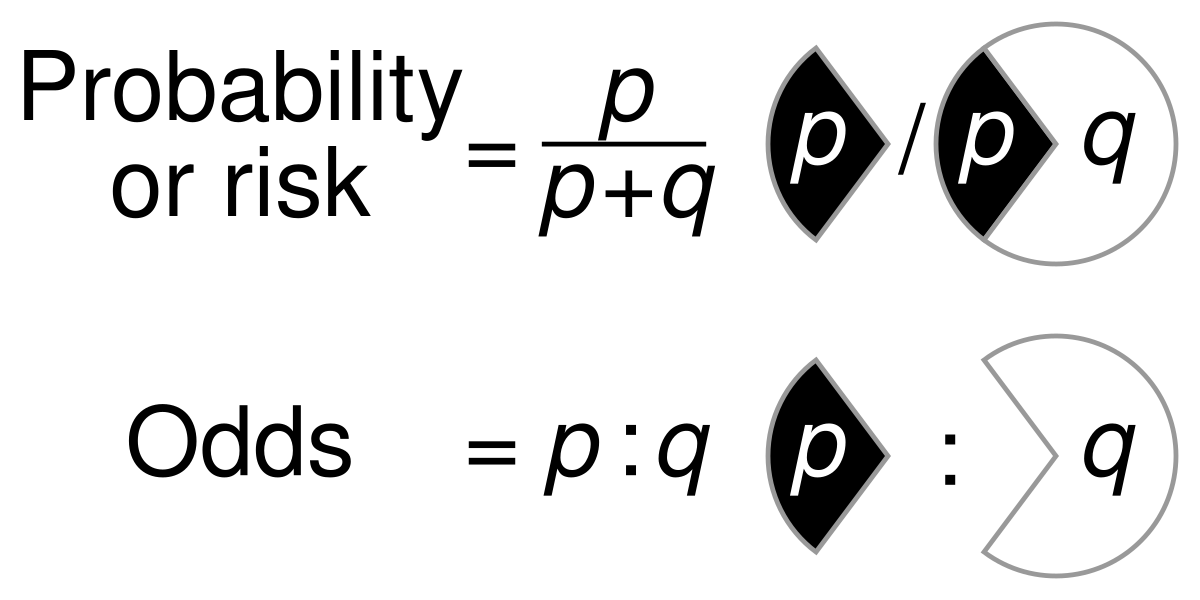



File Probability Vs Odds Svg Wikimedia Commons




Risk For In Hospital Complications Associated With Covid 19 And Influenza Veterans Health Administration United States October 1 18 May 31 Mmwr




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Example 8 29 Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios R Bloggers



The Difference Between Probability And Odds
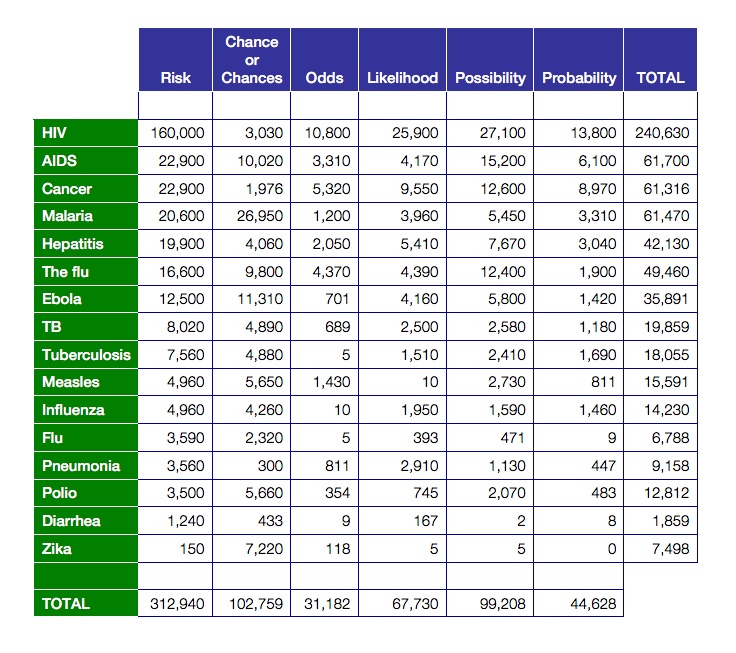



Risk Versus Chance What Are The Odds Health And Communications




Risks Of And Risk Factors For Covid 19 Disease In People With Diabetes A Cohort Study Of The Total Population Of Scotland The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
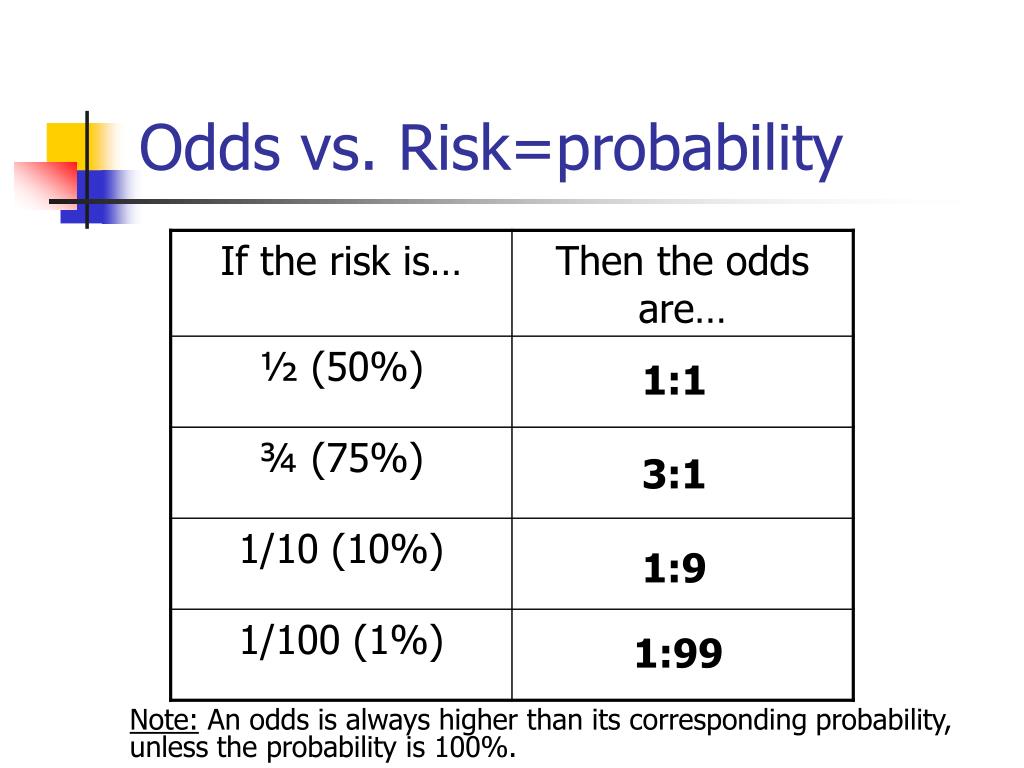



Ppt Conditional Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Interpretation Of Odds Ratio And Fisher S Exact Test By Sergen Cansiz Towards Data Science




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




View Image




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club




Solved Select All Of The True Statements Regarding The Odds Chegg Com



Summarising Binary Data Health Knowledge




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




What Are The Odds The Annals Of Thoracic Surgery




Odds Vs Risk Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Risk Versus Chance What Are The Odds Health And Communications




Association Of Folate Pathway Gene Polymorphisms With The Risk Of Prostate Cancer A Population Based Nested Case Control Study Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers Prevention




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk
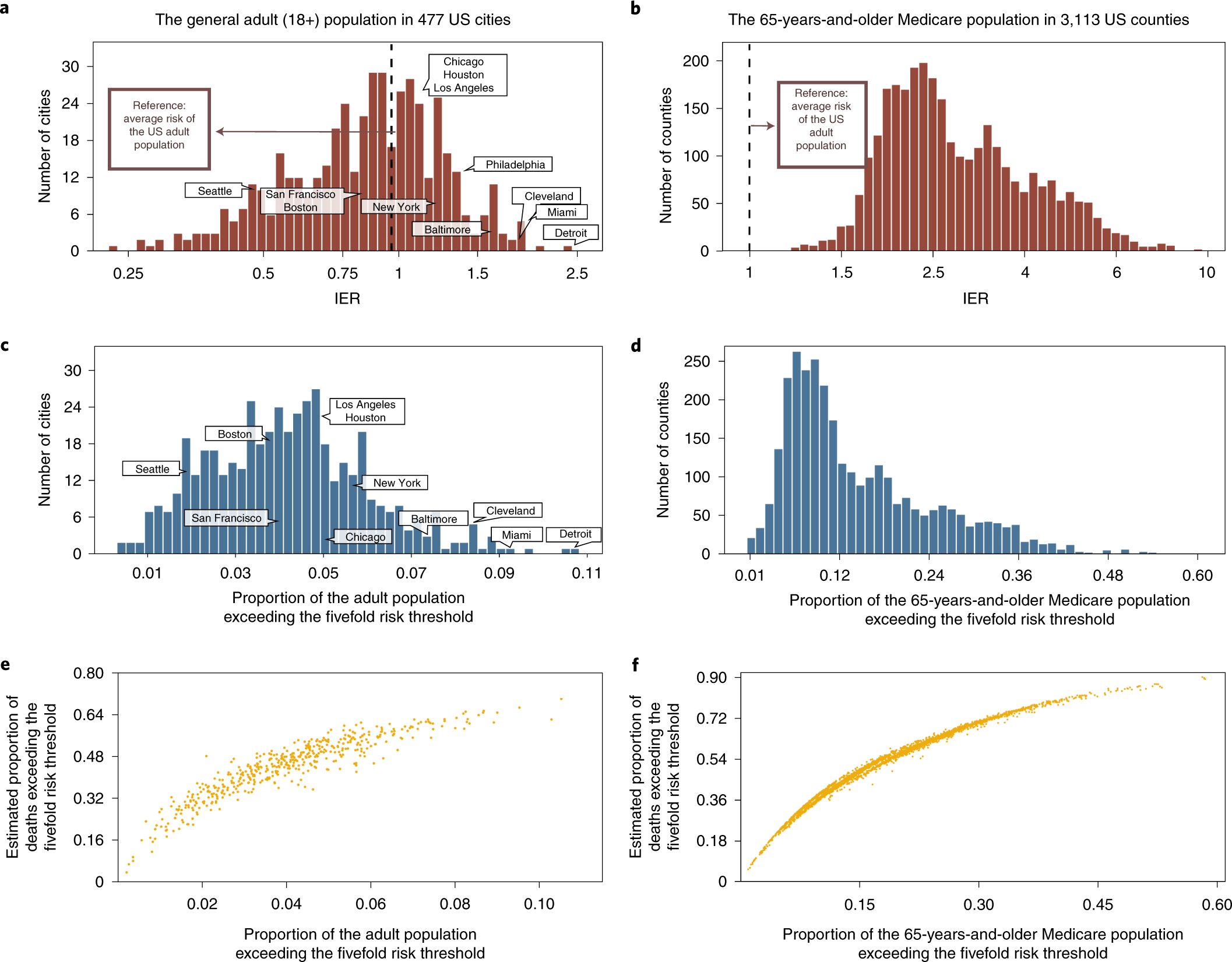



Individual And Community Level Risk For Covid 19 Mortality In The United States Nature Medicine



Plos One Different Depths Of Sedation Versus Risk Of Delirium In Adult Mechanically Ventilated Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis




Against All Odds Improving The Understanding Of Risk Reporting British Journal Of General Practice




The Odds Of Having The Disease Are In This Sample Of Chegg Com



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




What Are The Odds The Annals Of Thoracic Surgery




Table I From Prevalence Odds Ratio Versus Prevalence Ratio Choice Comes With Consequences Semantic Scholar




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Odds Ratio For Risk Factors Of Myocardial Infarction Worldwide In Old Download Scientific Diagram



Hazard Ratio




Is It Safe For Me To Go To Work Risk Stratification For Workers During The Covid 19 Pandemic Nejm



1




Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk Ranganathan P Aggarwal R Pramesh C S Perspect Clin Res



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj



What Are The Odds Stats With Cats Blog
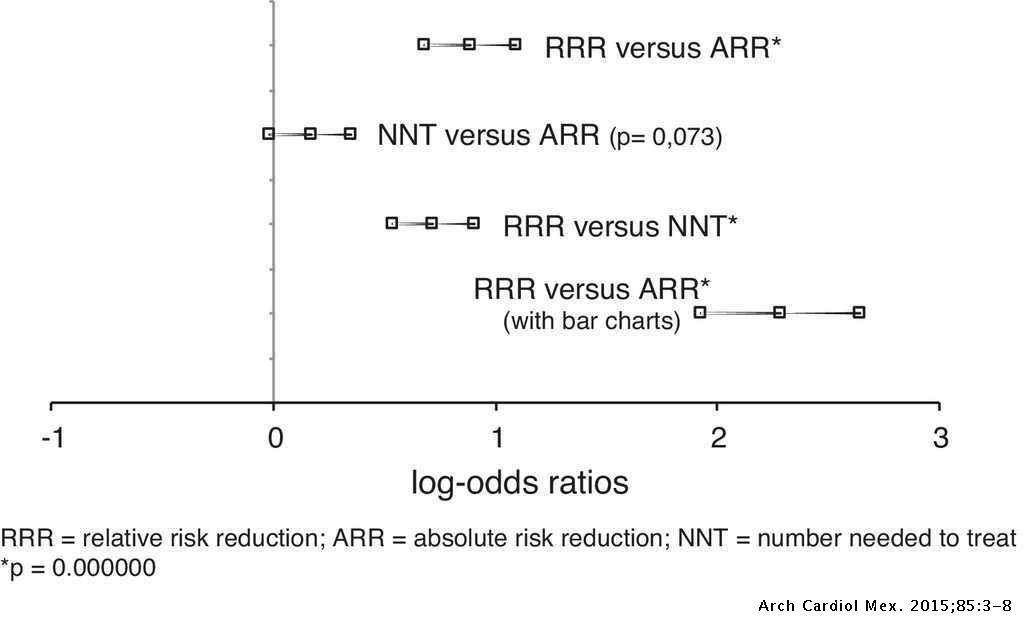



Effects Of Presenting Risk Information In Different Formats To Cardiologists A Latin American Survey Archivos De Cardiologia De Mexico




Figure 8 Risk Of Exacerbation Ics And Laba Controller And Quick Relief Versus Cbp Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroids And Long Acting Muscarinic Antagonists For Asthma Ncbi Bookshelf
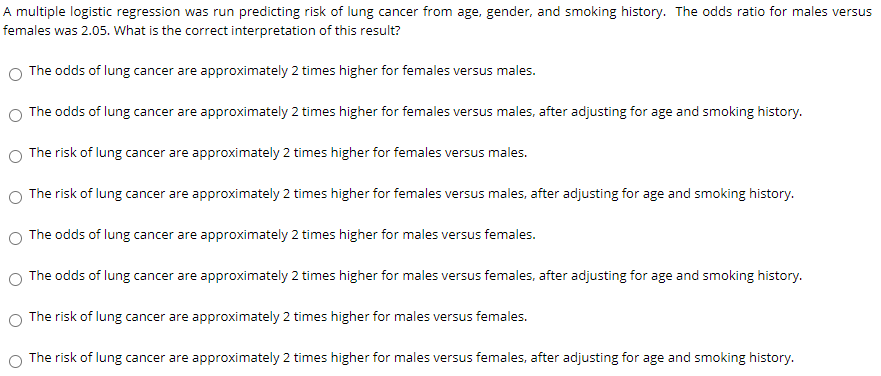



Solved A Multiple Logistic Regression Was Run Predicting Chegg Com




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Risk And Odds Ratios Losses Risk Categorical Data And Analyzing Accuracy Of Results Coursera



Solved True Or False Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Refer To A Contingency Table That Cross Classifies Subjects In Two Rows And Two Columns Labeled Success And Failure And For Which The Odds Ratio




Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk Ranganathan P Aggarwal R Pramesh C S Perspect Clin Res




Risk Factors And Disease Profile Of Post Vaccination Sars Cov 2 Infection In Uk Users Of The Covid Symptom Study App A Prospective Community Based Nested Case Control Study The Lancet Infectious Diseases




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals For Download Scientific Diagram




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Plos One Tumor Necrosis Factor Tnf Blocking Agents Are Associated With Lower Risk For Alzheimer S Disease In Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis And Psoriasis




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To




Figure B 6 Pooled Odds Ratios For Cardiac Anomalies For Sertraline Versus Placebo Maternal Fetal And Child Outcomes Of Mental Health Treatments In Women A Systematic Review Of Perinatal Pharmacologic Interventions




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios
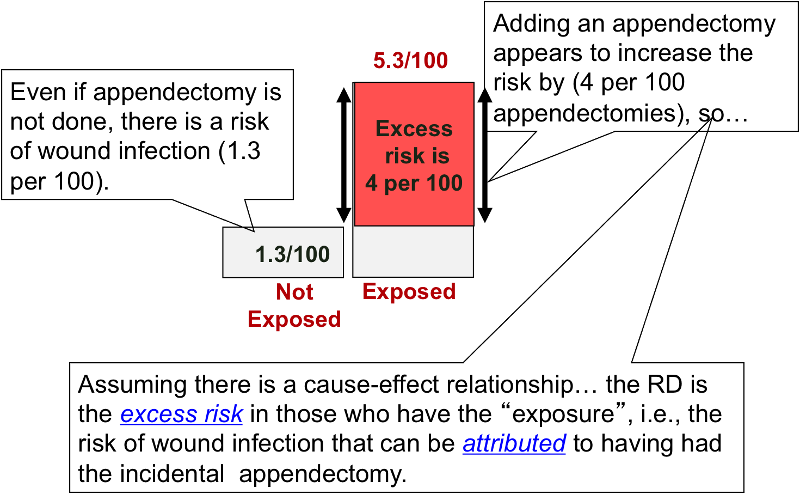



Risk Differences And Rate Differences




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk
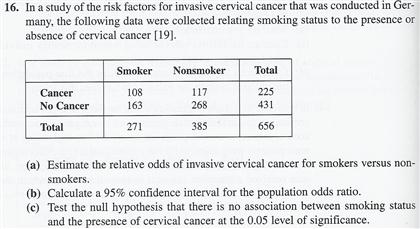



Solved In A Study Of The Risk Factors For Invasive Cervical Chegg Com




Single Workplace Factor Odds Ratios Between High Risk Versus Low Risk Download Table



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



Sh Lectures Qmp Odds Risks Ratios Studyingmed




The Response To Combination Therapy Treatment Regimens In Severe Difficult To Treat Asthma European Respiratory Society




Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute



Risk Of Death By Age And Sex



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk Pdf Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Outcomes Of Transcatheter Versus Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement In Low Risk Patients Heart Lung And Circulation




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Simple Rules On When And How To Use Them Mckenzie European Journal Of Clinical Investigation Wiley Online Library




Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj




Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney




Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube




Odds Ratio For Myocardial Infarction Risk Factors Worldwide Old 53 Download Scientific Diagram



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Versus Standard Dressings On Closed Incisions For The Prevention Of Surgical Site Infections After Vascular Surgery A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Of Randomized Controlled Trials European



1



1



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿